If a nation has an absolute advantage in producing a good, then it
A) will have a comparative advantage in producing that good.
B) will have no need to trade with other nations.
C) will always specialize in that good.
D) might or might not have a comparative advantage in producing that good.
E) will not have a comparative advantage in producing that good.
D
You might also like to view...
Refer to Table 7-6. If the actual terms of trade are 1 belt for 1.5 swords and 50 belts are traded, how many belts will Morocco gain compared to the "without trade" numbers?
A) 0 B) 10 C) 50 D) 60
The three methods for computing GDP include
a. the expenditure approach, the value-added approach, and the factor payments approach b. the expenditure approach, the value-added approach, and the productivity approach c. the productivity approach, the value-added approach, and the factor payments approach d. the expenditure approach, the productivity approach, and the factor payments approach e. the output approach, the productivity approach, and the factor payments approach
Mathematically, the marginal propensity to consume is
a. consumption divided by income. b. the change in consumption divided by the change in income. c. income divided by consumption. d. the change in income divided by the change in consumption.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 2.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow.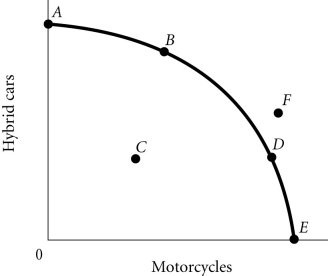 Figure 2.4According to Figure 2.4, Point F
Figure 2.4According to Figure 2.4, Point F
A. is efficient and attainable. B. cannot be produced with the current state of technology. C. represents underallocation of resources. D. represents what the people want.