In the short run, when a firm stops producing it:
A. must be that ATC is lower than market price.
B. can avoid earning profits less than zero.
C. avoids paying variable costs.
D. avoids paying fixed costs.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
The real business cycle theory and the new classical theory agree that
a. business cycles are driven by changes in aggregate demand. b. expectations are formed rationally. c. imperfect information plays a big role in business cycles. d. none of the above.
Average fixed costs in the short run:
A. increase as the quantity produced increases. B. decrease as the quantity produced increases. C. first decrease, then increase eventually as the quantity produced increases. D. first increase, then decrease eventually as the quantity produced increases.
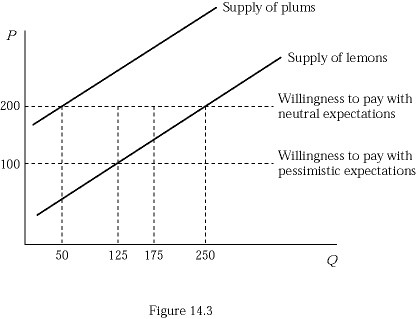 Figure 14.3 represents the market for used refrigerators. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $300 for a plum (high-quality) used refrigerator and $100 for a lemon (low-quality) used refrigerator. If buyers believe that 50% of used refrigerators in the market are lemons (low quality), how many plums (high quality) will be supplied by sellers?
Figure 14.3 represents the market for used refrigerators. Suppose buyers are willing to pay $300 for a plum (high-quality) used refrigerator and $100 for a lemon (low-quality) used refrigerator. If buyers believe that 50% of used refrigerators in the market are lemons (low quality), how many plums (high quality) will be supplied by sellers?
A. 50 B. 125 C. 175 D. 250
Grace Makutsi finally bought a pair of blue shoes that she had been coveting for a long time. In less than a week she discovered that the shoes were uncomfortable. Grace went back to wearing her old pair and stashed away the new pair. When asked by her
boss, Mme. Ramotswe, why does she not simply give away the new pair, she said: "But I paid so much for them." Grace's behavior A) is rational: she should not discard a valuable item. B) ignores the fact that the purchase price is now a sunk cost and has no bearing on whether she should give them away or not. C) supports the endowment effect which states that ownership of an item makes it more valuable. D) is rational because the more you pay for an item the more valuable it is.