A sequence of bases in the middle of an RNA used to encode a polypeptide has the sequence UUA—AUG—CGU. Is it possible to infer the sequence of the amino acids encoded by this RNA?
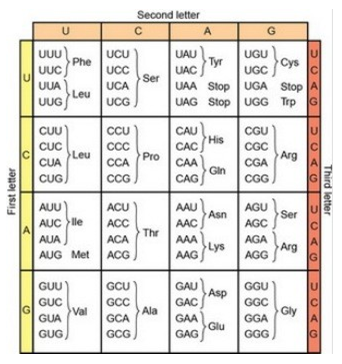
A) Yes, the sequence is Leu—Met—Arg.
B) Yes, the sequence is Asn—Tyr—Ala.
C) No, this RNA sequence could encode more than one amino acid sequence.
D) No; the sequence of amino acids in polypeptides is not related to the sequence of bases in RNA.
A) Yes, the sequence is Leu—Met—Arg.
You might also like to view...
ATP binding to myosin causes which of the following?
a. myosin binds to actin b. ADP and phosphorus disassociate c. myosin releases actin d. the filaments move toward the M line
Archaea and bacteria diverged approximately:
A) 3 billion years ago. B) 2 billion years ago. C) 4 billion years ago. E) 10,000 million years ago.
Suppose that a meteorite crashes into Earth and a sample of it is taken to a local research lab for analysis. Embedded several inches within the rocky structure, a microscopic cluster of dormant, spore-like structures is found
The scientists culture some of this material in a standard microbiological nutrient broth, and they are surprised to find many single-celled "organisms" moving around, growing, and reproducing in the broth. The "organisms" behave the same in both daylight and dark conditions, do not require oxygen, and thrive under a wide range of temperatures and pH levels. They stop moving, growing, and reproducing, however, when fewer nutrients are available in the medium. In this scenario, the "organisms" most closely resemble a(n) A) nonliving virus. B) autotrophic species of Eukarya. C) heterotrophic species of Eukarya. D) photosynthetic species of Bacteria. E) heterotrophic species of Archaea.
Which process results in quick bursts of change or speciation followed by long periods of stasis?
A. phyletic gradualism B. dynamic stasis C. punctuated equilibrium D. rocket evolution