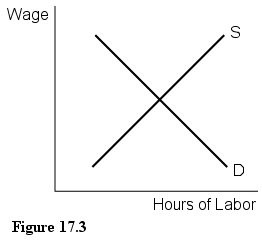
 Figure 17.3 describes the labor market for a manufacturing industry. In the short run, an increase in the productivity of the workers will:
Figure 17.3 describes the labor market for a manufacturing industry. In the short run, an increase in the productivity of the workers will:
A. cause the equilibrium wage and the hours of labor used to increase.
B. not have an effect on this market.
C. cause the equilibrium wage to increase but will not change the hours of labor used.
D. cause the equilibrium wage to increase and the hours of labor used to decrease.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Suppose that a technological decline makes labor less productive. What is likely to happen to wages and to potential output?
A) Wages decrease and potential output increases. B) Wages increase and potential output decreases. C) Wages increase and potential output increases. D) Wages decrease and potential output decreases.
Which of the following does not take place in the direct finance market?
A) Ownership in corporations is sold in the form of preferred stock. B) Ownership in corporations is sold in the form of common stock. C) Corporate bonds are sold to savers. D) Deposits from savers are accumulated and loans made to borrowers.
Refer to Figure 8.2. Holding other variables constant, a decrease in households' wealth will result in a
A) movement from point A to point B. B) movement from point B to point A. C) shift from curve S1 to curve S2. D) shift from curve S2 to curve S1.
Selling a good at a price determined by the intersection of the demand curve and the marginal cost curve is consistent with the (i) socially-optimal level of output. (ii) market solution for profit-maximizing competitive firms. (iii) market solution for a profit-maximizing monopoly
a. (i) and (ii) only b. (ii) and (iii) only c. (i) and (iii) only d. (i), (ii), and (iii)