A constant volume closed container of gas is at a pressure 1.00 × 105 N/m2 and a temperature 20°C. What is the pressure if the temperature of the gas is increased to 60.0°C?
A)
0.330 × 105 N/m2
B)
9.00 × 105 N/m2
C)
0.880 × 105 N/m2
D)
3.00 × 105 N/m2
E)
1.14 × 105 N/m2
E
You might also like to view...
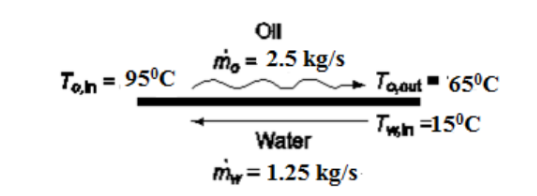
In a single-pass counterflow heat exchanger, 1.25 kg/s of water enter at 15°C and cools 2.5 kg/s of an oil having a specific heat of 2093 J/(kg K) from 95°C to 65°C. If the overall heat transfer coefficient is 280 W/(m2 K), determine the surface area required.
GIVEN
• Water cooling oil in a single-pass counterflow heat exchanger
• Water flow rate ( m w)= 1.25 kg/s
• Oil flow rate ( m o)= 2.5 kg/s
• Oil specific heat (cpo) = 2093 J/(kg K)
• Water inlet temperature (Tw, in) = 15°C
• Oil temperature
? To, in = 95°C
? To, out = 65°C
• Overall heat transfer coefficient (U) = 280 W/(m2 K)
FIND
• The surface area (A) required
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
the specific heat of water (cpw) = 4187 J/(kg K)
This photograph shows an interstellar bubble about 10 light-years in diameter. If you could photograph this same region about 100 years from now, how would you expect it to look different?
A) The bubble will be slightly larger. B) The bubble will be slightly smaller. C) The bubble will have burst as a supernova. D) The bubble's shape will have become much more like an oval rather than a sphere.
Which of the following describes a major danger of interstellar travel at near-light speed?
A) Atoms and ions in interstellar space will hit a fast-moving spacecraft like a flood of dangerous cosmic rays. B) Any interstellar journey will take much longer than the lives of the crew members. C) Time dilation will slow the heart beats of the crew to a dangerously low rate. D) Asteroid fields floating in interstellar space will present a navigational challenge.
Car A rear ends Car B, which has twice the mass of A, on an icy road at a speed low enough so that the collision is essentially elastic. Car B is stopped at a light when it is struck. Car A has mass m and speed v before the collision. After the collision
a. each car has half the momentum. b. car A stops and car B has momentum mv. c. car A stops and car B has momentum 2mv. d. the momentum of car B is four times as great in magnitude as that of car A. e. each car has half of the kinetic energy.