Compare the features of the classical economic model to the Keynesian economic model. How do these models influence the aggregate demand curve and the aggregate supply curve? Which model, in your opinion, benefits the economy in the long run?
Answer: The major difference is the role government plays in each. Classical economics is essentially free-market economics, which maintains that government involvement in managing the economy should be limited as much as possible. Keynesian economics espouses the view that government should take an active role in managing the economy, particularly in depression/recession like periods.
Adam Smith is widely acknowledged as the founder of the classical school of thought while the founder of the Keynesian school is of course John Maynard Keynes.
This difference leads to different conclusions about economic phenomena, some of the more important ones are:
Unemployment: The causes of unemployment are viewed differently. Classicists believe unemployment is caused by supply-side factors (the level of investment, the level of capital, the productivity of labour etc). Keynesians place greater emphasis on falling demand as a cause of unemployment.
Wages and Prices: Classicists believe wages and prices are flexible and so in the long term, the economy will maintain full employment, full employment meaning anybody looking for a job can find one. Keynesians maintain that wages and prices can be sticky and hence an economy can find itself in a situation where there is less than full employment for significant periods of time.
Rationality: Classicists believe that people are rational and make economic decisions that can be described as enlightened self-interest. Keynesians argue that in difficult times, people give in to irrational fears that overwhelm sensible decision making. This could lead to falls in consumer confidence that could last a long time without government intervention
You might also like to view...
To secure a charter, the deciding bodies required which of the following from the business enterprises?
(a) A statement of business purpose and location (b) A business plan (c) A description of capital and labor requirements and expectations (d) All of the above
Fiona uses all of her income to purchase popcorn and butter. At any two points A and B on Fiona’s budget constraint,
a. Fiona is equally happy.
b. Fiona is spending more money on popcorn than she is spending on butter.
c. Fiona's income is different.
d. the price of popcorn relative to the price of butter is the same.
For a given decrease in supply, the condition of demand that will result in the most significant change in quantity is when demand is
A. inelastic. B. perfectly inelastic. C. perfectly elastic. D. elastic.
Refer to the graph shown. Assume the economy is in short-run equilibrium at point A below potential output. The government opts for an expansionary fiscal policy in an attempt to pull the economy out of the recession. Not considering shifts in aggregate supply, an economist with a functional finance view, who also believes in a full crowding out effect, would conclude that the economy will end up at point: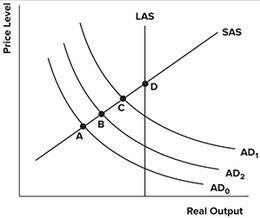
A. A. B. B. C. C. D. D.