Which of the following is FALSE about public-sector decision making?
A. The price charged to consumers is often less than its full opportunity cost.
B. Decisions are based on majority rule.
C. Incentives play a role in decision making.
D. Decisions involve no opportunity cost.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Trade requires:
A. governments to get together and agree on who is going to specialize in what. B. governments employ an economic planner to find comparative advantage for different products. C. that day-to-day business decision making is carried out almost entirely by firms and individuals, not by governments. D. firms and individuals to follow government mandates about what to trade.
The institution that sets the nation's monetary policy is called the
PriceQuantity Demanded$510$420$330$240$150Refer to the table above. Starting at a $1 price, at what price range does demand become elastic?
A. $4-5 B. $3-4 C. $1-2 D. $2-3
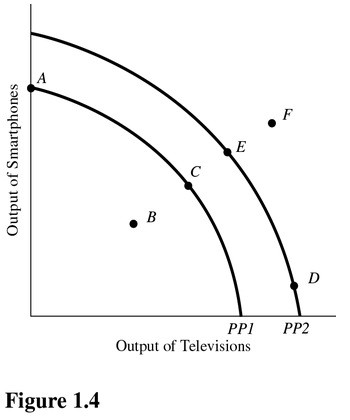 Which of the following is true about the combination of televisions and smartphones represented by point F in Figure 1.4?
Which of the following is true about the combination of televisions and smartphones represented by point F in Figure 1.4?
A. Point F is unattainable even with advances in technology. B. Point F will be more easily attainable if the government takes control of all privately run factories. C. Point F is inefficient now. D. Point F can possibly be reached if more economic resources become available or technology improves.