Ketosis develops in the postabsorptive state. What is ketosis? Why does it develop? What metabolic effects does it have?
Ketosis is a high concentration of ketone bodies in body fluids. Ketone bodies are metabolites with the ketone group that form during starvation states. When glucose levels are low, the liver turns to fats and amino acids to provide energy. This produces much acetyl-CoA, which leads to production of ketone bodies. Because most ketone bodies are acidic, they lower the pH of body fluids, bringing on acidosis. If severe, the ketosis and acidosis can injure the CNS, heart, and other organs. In extreme cases, death can result.
You might also like to view...
Which of the following statements regarding NK cells is a false or incorrect statement?
A) NK cells are a type of neutrophil. B) NK cells are present in the blood, spleen, lymph nodes, and red bone marrow. C) NK cells attack cells that display abnormal MHC antigens. D) NK cells attack cancer cells and virus-infected body cells.
As carbon dioxide enters systemic blood, it causes more oxygen to dissociate from hemoglobin (the Haldane effect), which in turn allows more CO2 to combine with hemoglobin and more bicarbonate ions to be generated (the Bohr effect)
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Using Figure 26.3, match the following:
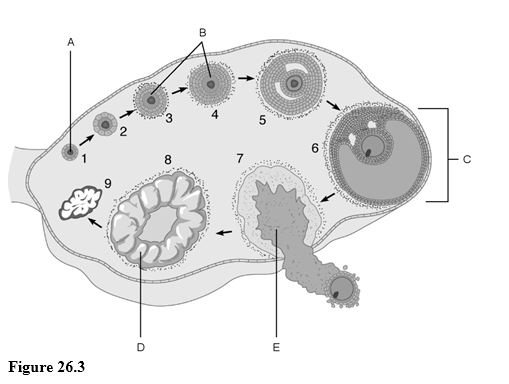
1) The stage called ovulation.
2) Vesicular (Graafian) follicle.
3) Primary follicles.
4) Primordial follicle.
5) Corpus luteum.
6) Mature follicle.
Which is a hormonal response to a stressful situation?
A. Negative feedback from cortisol increases secretion of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). B. Secretion of aldosterone by the adrenal gland is decreased. C. Negative feedback from cortisol increases the secretion of corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH). D. Plasma levels of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) decrease. E. Plasma levels of cortisol increase.