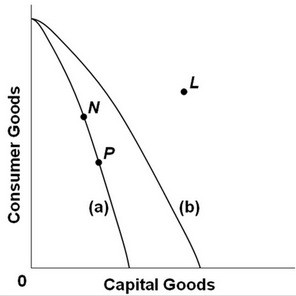
 Refer to the above production possibilities curves. Curve (a) is the current curve for the economy. Other things being equal, society's current choice of point P on curve (a) will:
Refer to the above production possibilities curves. Curve (a) is the current curve for the economy. Other things being equal, society's current choice of point P on curve (a) will:
A. entail a slower rate of economic growth than would the choice of point N.
B. be unobtainable because it exceeds the productive capacity of the economy.
C. allow it to achieve more rapid economic growth than would the choice of point N.
D. entail the same rate of growth as would the choice of point N.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
When the economy is operating at a point where aggregate demand equals short-run aggregate supply, it must be true that:
A. aggregate demand also equals long-run aggregate supply. B. the short-run level of output is not the same as long-run potential output. C. prices are higher than expected prices. D. None of these must be true.
Resources are used more efficiently if people, regions, and countries specialize in goods for which they have a(n): a. disincentive to trade with others
b. higher opportunity cost. c. absolute advantage in production. d. comparative advantage in production.
Spending by consumers on consumption goods, spending by businesses on investment goods, spending by government, and spending by foreigners on net exports make up
a. disposable national income b. the equilibrium economy c. aggregate supply d. aggregate expenditure e. discretionary spending
Which of the following is an example of consumption?
a. The town council of Oak City pays the salaries of its employees. b. The stores in Oak City expand their inventories of goods for sale. c. The residents of Oak City buy thousands of hotdogs over a holiday weekend. d. The manufacturers in Oak City spend millions of dollars on new robotic machines.