A large open economy has desired national saving of Sd = 20 + 200rw, and desired national investment of Id = 30 - 200rw. The foreign economy has desired national saving of 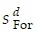 = 40 + 100rw, and desired national investment of
= 40 + 100rw, and desired national investment of 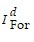 = 75 - 400rw.(a)Calculate the equilibrium values of rw, CA, CAFor, S, I, SFor, and IFor.(b)Suppose Sd rises by 45, so that now Sd = 65 + 200rw. Calculate the equilibrium values of rw, CA, CAFor, S, I, SFor, and IFor.(c)Suppose, with Sd back to Sd = 20 + 200rw, as in part (a), that Id rises by 45, to Id = 75 - 200rw. Calculate the
= 75 - 400rw.(a)Calculate the equilibrium values of rw, CA, CAFor, S, I, SFor, and IFor.(b)Suppose Sd rises by 45, so that now Sd = 65 + 200rw. Calculate the equilibrium values of rw, CA, CAFor, S, I, SFor, and IFor.(c)Suppose, with Sd back to Sd = 20 + 200rw, as in part (a), that Id rises by 45, to Id = 75 - 200rw. Calculate the
equilibrium values of rw, CA, CAFor, S, I, SFor, and IFor.
What will be an ideal response?
| (a) | In equilibrium, Sd + 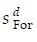 = Id + = Id + 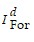 so that 60 + 300rw = 105 - 600rw, or 900rw = 45, so rw = so that 60 + 300rw = 105 - 600rw, or 900rw = 45, so rw = |
| (b) | Now 900rw = 0, so rw = 0.0. Using this in the formulas, we get S = 65, I = 30, CA = 35, SFor = 40, |
| (c) | Now 900rw = 90, so rw = 0.10. Using this in the formulas, we get S = 40, I = 55, CA = -15, SFor = |
Notice that the current account may swing from positive to negative, depending on the value of the real interest rate.
You might also like to view...
When consumers spend and buy things regardless of their level of income, this is known as
A) bad financial management. B) using credit to its maximum. C) living the good life. D) autonomous consumption spending.
In the Keynesian model, suppose the Fed sets a target for the real interest rate. If the IS curve shifts down and to the left, and the Fed wants to keep output unchanged in the short run and the price level unchanged in the long run, it will
A) shift the LR curve up. B) not shift the LR curve. C) shift the LR curve down. D) shift the IS curve up and to the right.
Which of the following countries has a low level of trade by world standards but has typically shown large trade surpluses in recent decades?
a. United States b. Brazil c. Japan d. France
The money demand curve shifts to the left when the Fed buys government bonds
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false