A system consisting of a positively-charged particle and an electric field
A. loses potential difference and kinetic energy when the charged particle moves in the direction of the field.
B. loses electric potential energy when the charged particle moves in the direction of the field.
C. loses kinetic energy when the charged particle moves in the direction of the field.
D. gains electric potential energy when the charged particle moves in the direction of the field.
E. gains potential difference and electric potential energy when the charged particle moves in the direction of the field.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Of the three types of nuclear decay, only __________ does not affect the atomic number of the nucleus
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Another name for solid carbon dioxide is
a. heavy water. b. Epsom salt. c. dry ice. d. quicksilver.
A 2000 kg car accelerates up to a velocity of 40 m/s in 5.0 seconds. The brakes are applied, and the car is brought to a stop. The work done by the friction in the brakes is
A. 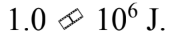
B. 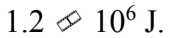
C. 
D. 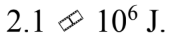
E. 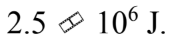
The decay rate of a radioactive sample decreases from 175 kBq to 12.4 kBq in 18.3 s. What is the half-life of this sample?
What will be an ideal response?