The purchasing power parity theory is a reasonably good explanation for nominal exchange rate determination:
A. in the short run.
B. in the long run.
C. when there are fixed exchange rates.
D. when there are significant volumes of non-traded goods and services.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
A steady-state equilibrium refers to:
A) an equilibrium in which the stock of physical capital remains constant over time. B) an equilibrium in which the inequality remains constant over time. C) an equilibrium in which the GDP per capita remains constant over time. D) an equilibrium in which the poverty rate remains constant over time.
All of the following are possible outcomes of a banking crisis EXCEPT
A) depositors, but not banks, may lose all or a portion of their assets. B) a recession due to decreases in consumption by households. C) decreases in lending practices by banks. D) decreases in investment. E) a contagion effect of the crisis from vulnerable banks to financial institutions on sound basis.
Diseconomies of scale exist over the range of output for which the long-run average cost curve is:
a. constant. b. falling. c. rising. d. none of these.
Refer to the graph shown. The least-cost method of producing 1,000 units of output is shown at point: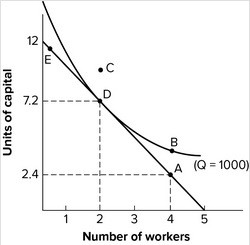
A. A. B. B. C. C. D. D.