Demand for farm products, in general, is said to be relatively price inelastic. Therefore, U.S. farm policy, which is designed to keep farm prices above equilibrium, should
a. decrease farm incomes
b. increase farm incomes
c. not affect farm incomes
d. reduce the number of farmers
e. lower food prices for consumers
B
You might also like to view...
Refer to Table 4-4. Suppose that the quantity of labor demanded increases by 40,000 at each wage level. What are the new free market equilibrium hourly wage and the new equilibrium quantity of labor?
A) W = $8.00; Q = 390,000 B) W = $9.50; Q = 380,000 C) W = $10.00; Q = 390,000 D) W = $8.50; Q = 380,000
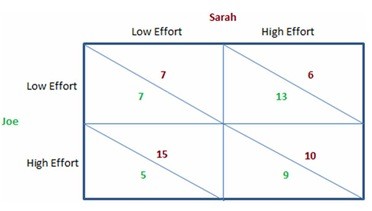 This figure shows the payoffs involved when Sarah and Joe work on a school project together for a single grade. They both will enjoy a higher grade when more effort is put into the project, but they also get pleasure from goofing off and not working on the project. The payoffs can be thought of as the utility each would get from the effort they individually put forth and the grade they jointly receive.According to the figure shown, Sarah:
This figure shows the payoffs involved when Sarah and Joe work on a school project together for a single grade. They both will enjoy a higher grade when more effort is put into the project, but they also get pleasure from goofing off and not working on the project. The payoffs can be thought of as the utility each would get from the effort they individually put forth and the grade they jointly receive.According to the figure shown, Sarah:
A. should put forth low effort, regardless of what Joe chooses to do. B. should take the first-mover advantage and put forth low effort. C. should put forth high effort, regardless of what Joe choose to do. D. does not have a dominant strategy.
Which of the following statements is correct about the demand curve of the perfectly competitive industry?
A) The demand curve of the perfectly competitive industry is horizontal as are the demand curves facing the individual firms. B) The market demand curve of perfect competition is vertical because the individual consumers are buying a homogeneous product. C) The market demand curve of the perfectly competitive industry is downward sloping while the demand curve facing an individual firm is horizontal. D) The market demand curve of the perfectly competitive industry is downward sloping, so the demand curves of the individual firms are also downward sloping.
According to the text, minimum-wage laws cause increases in
A. productivity. B. employment possibilities. C. poverty. D. structural unemployment.