N-Step SCAN differs from F-SCAN in that ________.
a) N-Step SCAN prevents indefinite postponement, but F-SCAN does not.
b) N-Step SCAN always provides higher throughput than F-SCAN, but results in a larger variance in response times.
c) N-Step SCAN selects requests it will service during the current sweep according to the number of requests; F-SCAN selects such requests according to time.
d) None of the above—N-Step SCAN and F-SCAN are identical.
c) N-Step SCAN selects requests it will service during the current sweep according to the number of requests;
You might also like to view...
Calculate temperature (degrees F and C) at a given depth inside the earth (km)
What will be an ideal response?
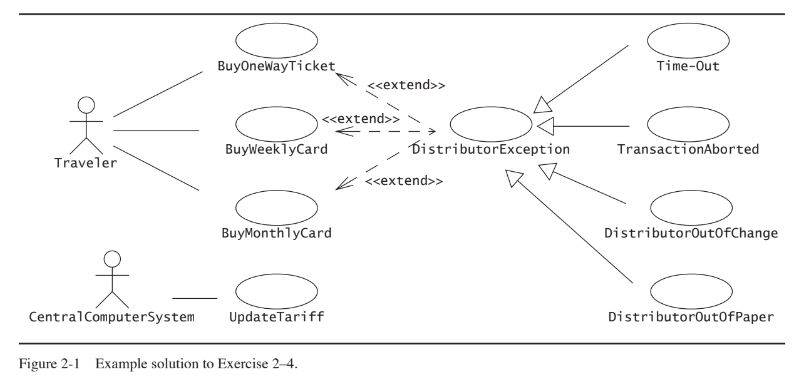
Draw a use case diagram for a ticket distributor for a train system. The system includes two actors: a traveler, who purchases different types of tickets, and a central computer system, which maintains a reference database for the tariff. Use cases should include: BuyOneWayTicket, BuyWeeklyCard, BuyMonthlyCard, UpdateTariff. Also include the following exceptional cases: Time-Out (i.e., traveler took too long to insert the right amount), TransactionAborted (i.e., traveler selected the cancel button without completing the transaction), DistributorOutOfChange, and DistributorOutOfPaper.
When used in a menu name, the asterisk character is used to indicate that a character is a hot key.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
A security administrator is trying to encrypt communication. For which of the following reasons should administrator take advantage of the Subject AlternativeName (SAM) attribute of a certificate?
A. It can protect multiple domains B. It provides extended site validation C. It does not require a trusted certificate authority D. It protects unlimited subdomains