Air is heated from 20°C to 100°C. Determine the change in specific internal energy and the change in specific enthalpy for the air, assuming ideal gas with constant specific heat behavior.
Given: T1 = 20°C; T2 = 100°C
What will be an ideal response?
Properties for air: cp = 1.005 kJ/kg-K, cv = 0.718 kJ/kg-K at 300 K.
For an ideal gas with constant specific heats:
?u = cv (T2 – T1) = (0.718 kJ/kg-K) (100°C – 20°C) = 57.4 kJ/kg
?h = cp (T2 – T1) = (1.005 kJ/kg-K) (100°C – 20°C) = 80.4 kJ/kg
Recall that the change in °C is the same numerically as the change in K, for the temperature.
You might also like to view...
What is the most important part of the fuel cell stack and what is its purpose?
What will be an ideal response?
The Equal Rights Amendment (ERA) failed to be ratified by the needed 38 states largely because
A. the Catholic Church opposed it. B. many Americans realized that its goals had already been achieved without amending the Constitution. C. an anti-feminist backlash led by Phyllis Schlafly stirred sufficient opposition to stop it. D. many suspected that it would require such things as rigid quotas and unisex bathrooms. E. many Americans believed that equal gender treatment was a matter of changing attitudes, not creating laws.
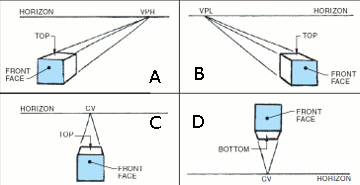 In the accompanying figure, the item identified with the letter C is ____.
In the accompanying figure, the item identified with the letter C is ____.
A. the right vanishing point B. an object below the center of vision C. an object above the center of vision D. the left vanishing point
Express 4/15 as a decimal, rounded to the nearest thousandth as necessary.
What will be an ideal response?