In regression analysis, the explanatory variables
A) are always price and income.
B) are the variables whose variations are to be explained.
C) are the factors that are thought to affect the dependent variable.
D) are used to explain the random error term.
C
You might also like to view...
According to polling data, Americans believe that after-tax corporate profits are
A. less than 10 percent of corporate product prices. B. nearly 50 percent of the corporate product price. C. approximately 36 percent of corporate product prices. D. approximately 25 percent of corporate product prices.
Economists have long debated whether there is a significant loss of well-being to society in markets that are monopolistically competitive rather than perfectly competitive
Which of the following offers the best reason why some economists believe that monopolistically competitive markets are less efficient than perfectly competitive markets? A) In contrast to perfectly competitive markets, firms in monopolistically competitive markets can charge a price greater than average total cost in the short run. B) In contrast to perfectly competitive markets, firms in monopolistically competitive markets do not produce where price equals average total cost in long-run equilibrium. C) In contrast to perfectly competitive markets, neither allocative efficiency nor productive efficiency are achieved in monopolistically competitive markets. D) In contrast to perfectly competitive markets, firms in monopolistically competitive markets earn economic profits in long-run equilibrium.
The practice of securitization of mortgages:
A. pooled high-risk mortgages together, which raised the prices of them to investors. B. allowed investors to profit from the mortgage payments without being exposed to any risk. C. pooled the risk of mortgages, allowing higher risk mortgages to be more safely sold to investors. D. was undertaken by government to guarantee the values of real estate.
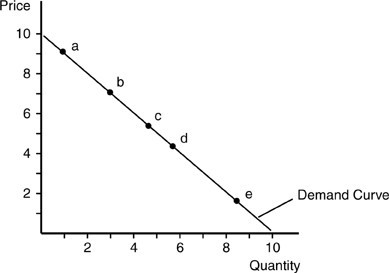 In the above figure, along which range would the demand for this good be most elastic?
In the above figure, along which range would the demand for this good be most elastic?
A. between point c and point d B. between point d and point e C. between point a and point b D. at point e