The solar constant is a measure of
a. the amount of solar energy reaching Earth.
b. the length of the sunspot cycle.
c. the period of rotation of the Sun's equator.
d. the average number of sunspots seen during the Maunder minimum.
e. the Sun's mass.
Ans: a. the amount of solar energy reaching Earth.
You might also like to view...
Conduction: A heat-conducting rod that is wrapped in insulation is constructed with a 0.15-m length of alloy A and a 0.40-m length of alloy B, joined end-to-end. Both pieces have cross-sectional areas of 0.0020 m2. The thermal conductivity of alloy B is known to be 1.8 times as great as that for alloy A. The end of the rod in alloy A is maintained at a temperature of 10°C, and the other end of the rod is maintained at an unknown temperature. When steady state flow has been established, the temperature at the junction of the alloys is measured to be 40°C, and the rate of heat flow in the rod is measured at 56 W. What is the temperature of the end of the rod in alloy B?
A. 80°C B. 84°C C. 88°C D. 92°C E. 96°C
Fig. 15-5 shows four Gaussian surfaces surrounding a distribution of charges. Which Gaussian surfaces have an electric flux of +q/?o through them?
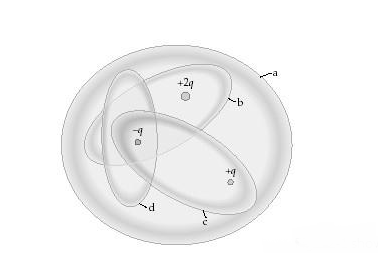
(1) a.
(2) b.
(3) b and d.
(4) c.
(5) b and c.
A gray (Gy) is
A) 3.70 × 1010 decays/s in radium. B) the SI unit of absorbed dose = 1 J/kg = 100 rad. C) a dosage of 2.58 × 10-4 C/kg. D) the SI unit of radioactivity (= 1 decay/s). E) 10-2 J/kg.
To say that an object is being accelerated, means that
1) it is at rest, 2) it is moving, 3) it is either at a state of rest or a state of constant velocity, 4) its state of motion is changing, and we define acceleration to be 5) a change in speed. 6) a change in velocity. 7) the rate at which speed changes. 8) the rate at which velocity changes.