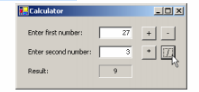
(Simple Calculator Application) In this exercise, you will add functionality to a simple calculator application. The calculator will allow a user to enter two numbers in the Text- Boxes. There will be four Buttons—labelled +, -, / and *. When the user clicks the Button labelled as addition, subtraction, multiplication or division, the application will perform that operation on the numbers in the TextBoxes and display the result. The calculator also should clear the calculation result when the user enters new input. displays the com- pleted calculator.
a) Copying the template to your working directory.
b) Opening the application’s template file.
c) Coding the addition Click event handler.
d) Coding the subtraction Click event handler.
e) Coding the multiplication Click event handler.
f) Coding the division Click event handler.
g) Clearing the result.
h) Running the application.
i) Closing the application.
a) Copy the directory C:\Examples\
Tutorial06\Exercises\SimpleCalculator to your C:\SimplyCSP directory.
b) Double click SimpleCalculator.sln in
the SimpleCalculator directory to open the application.
c) This event handler should add the two numbers and display the result.
d) This event handler should subtract the
second number from the first number and display the result.
e) This event handler should multiply the two numbers and display the result.
f) Write event handlers for the TextBoxes’ TextChanged events.
Write code to clear the result Label (lblResult) after the user enters new input into
either TextBox.
h)Select Debug > Start to run your application. Enter a first
number and a second number, then verify that each of the Buttons works by clicking each, and viewing the output. Repeat this process with two new values and again ver-ify that the proper output is displayed based on which Button is clicked.
i) Close your running application by clicking its close box.
You might also like to view...
Newton's method is likely to diverge if the initial guess is close to a value at which
a. the sign of the function value changes b. the first derivative of the function evaluates to zero c. the function evaluates to zero d. no valid completion: Newton's method always converges.
Consider the following class definition.public class Rectangle{ private double length; private double width; public Rectangle() { length = 0; width = 0; } public Rectangle(double l, double w) { length = l; width = w; } public void set(double l, double w) { length = l; width = w; } public void print() { System.out.println(length + " " + width); } public double area() { return length * width; } public double perimeter() { return 2 * length + 2 * width; }}Which of the following statements correctly instantiates the Rectangle object myRectangle?(i)
myRectangle = new Rectangle(12.5, 6); (ii) Rectangle myRectangle = new Rectangle(12.5, 6);(iii) class Rectangle myRectangle = new Rectangle(12.5, 6); A. Only (i) B. Only (ii) C. Only (iii) D. Both (ii) and (iii)
Which of the following is NOT a type of multi-user computer?
A. Embedded system B. Mainframe computer C. Supercomputer D. Network server
 Item D in the accompanying figure shows that the page sizes are measured in _______________ .
Item D in the accompanying figure shows that the page sizes are measured in _______________ .
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).