Suppose the population of a country falls, but its Real GDP remains constant. As a result, there is __________ economic growth
A) both absolute economic growth and per-capita real
B) absolute economic growth, but not per-capita real
C) per-capita real economic growth, but not absolute
D) neither absolute economic growth nor per-capita real
C
You might also like to view...
At the point at which the consumption function intersects the 45 degree reference line
A) planned real consumption of real disposable income equals zero. B) planned real saving equals real disposable income. C) planned real consumption equals real disposable income. D) equilibrium output is supply determined equilibrium output is determined by both.
Suppose the economy's production function is Y = A(300N – N2). The marginal product of labor is MPN = A(300 - 2N). Suppose that A = 10. The supply of labor is NS = 0.05w + 0.005G
(a) If G is 26,000, what are the real wage, employment, and output? (b) If G rises to 26,400, what are the real wage, employment, and output? (c) If G falls to 25,600, what are the real wage, employment, and output? (d) In cases (b) and (c), what is the government purchases multiplier; that is, what is the change in output divided by the change in government purchases?
The rationality assumption says that
A) people do not intentionally make decisions that would leave them worse off. B) people never make decisions that would leave them worse off. C) people do not respond to incentives since incentives require scarce resources. D) all economic analysis must be normative.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 2.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow.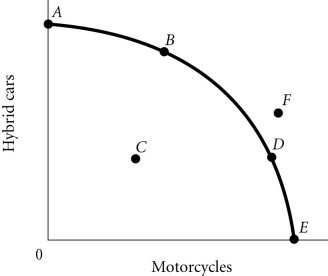 Figure 2.4According to Figure 2.4, as the economy moves from Point B to Point D, the opportunity cost of motorcycles, measured in terms of hybrid cars,
Figure 2.4According to Figure 2.4, as the economy moves from Point B to Point D, the opportunity cost of motorcycles, measured in terms of hybrid cars,
A. increases B. remains constant. C. initially increases, then decreases. D. decreases.