Two identical masses are attached by a light string that passes over a small pulley, as shown in Figure 6-6. The table and the pulley are frictionless. The masses are moving
A. with an acceleration equal to g.
B. with an acceleration less than g.
C. with an acceleration greater than g.
D. at constant speed.
E. with an acceleration that cannot be determined without additional information.
Ans: B. with an acceleration less than g.
You might also like to view...
The ________ cycle of the phases of the Moon is due to the Moon's spherical shape and the ______ shining on it from different directions
a. monthly; Earth b. yearly; Earth c. monthly; Sun d. yearly; Sun
RC Circuits: A charged capacitor is connected in series with a resistor and an open switch. At time t = 0 s, the switch is closed. Which of the graphs below best describes the potential difference V across the capacitor as a function of time t?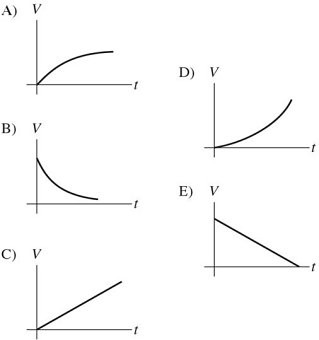
A. A B. B C. C D. D E. E
The bending of waves as they pass the
sharp edge of an object is called a) polarization. b) dispersion. c) refraction. d) diffraction. •
Spectral lines from Galaxy B are redshifted from their rest wavelengths twice as much as the spectral lines from Galaxy A. According to Hubble's law, what can you say about their approximate relative distances?
A) Galaxy A is twice as far as Galaxy B. B) Galaxy B is four times as far as Galaxy A. C) Galaxy A is four times as far as Galaxy B. D) Galaxy B is twice as far as Galaxy A. E) Not enough information to say—you need to know Hubble's constant to answer this question.