Suppose that a market for a product is in equilibrium at a price of $3 per unit. At any price below $3 per unit:
A. there will be an excess demand for the product.
B. there will be an excess supply of the product.
C. the quantity demanded of the product will be less than the quantity supplied of that product.
D. there will be a surplus of that product.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
The fact that output gaps will not last indefinitely, but will be closed by rising or falling inflation is the economy's:
A. income-expenditure multiplier. B. self-correcting property. C. short-run equilibrium property. D. long-run equilibrium property.
As a source of funds for nonfinancial businesses, stocks are relatively more important in
A) the United States. B) Germany. C) Japan. D) Canada.
Under the adaptive expectations hypothesis, which of the following is the effect of a shift to a more expansionary monetary policy?
A. In the short run, the real rate of output will be unaffected, but in the long run, it will increase. B. In the short run, the unemployment rate will decrease, but in the long run, it will self correct to the natural rate of unemployment. C. There will be a permanent increase in the real rate of output, but the inflation rate will also be a little higher. D. In the short run, the impact on the real rate of output is uncertain, but in the long run, output will increase.
The question below are based on the following four sets of data-pairs: (1) A and B, (2) C and D, (3) E and F, and (4) G and H. In each set, the independent variable is in the left column and the dependent variable is in the right column
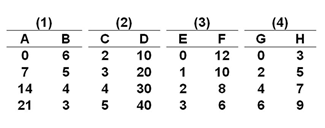
The slope of the linear graph that pictures data set 2 above is:
A. .10
B. 20
C. 5
D. 10