The actual multiplier effect in the U.S. economy is less than the multiplier effect in the text examples because:
A. the real-world MPS is larger than the MPS in the examples.
B. in addition to saving, households use some of any increase in income to buy imported
goods and to pay additional taxes.
C. the gap between the nominal interest rate and the real interest rate widens as the economy
expands or contracts.
D. the MPC in the United States is greater than 1.
B. in addition to saving, households use some of any increase in income to buy imported
goods and to pay additional taxes.
You might also like to view...
When household incomes are ranked from lowest to highest, the middle income is known as the:
A) median income. B) mean income. C) means-tested income. D) official poverty level. E) transfer income.
If there was a positive technological shock which increased the demand for labor, then
A) imports would increase. B) GDP would decrease. C) GDP would increase. D) imports would decrease.
Using Figure 1 below, if the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD2 to AD3 the result in the short run would be:
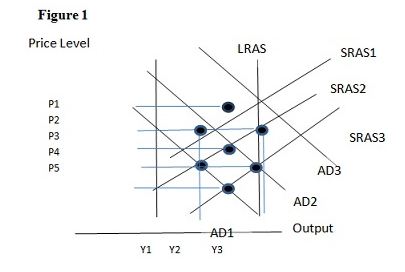
A. P1 and Y2.
B. P3 and Y1.
C. P2 and Y3.
D. P2 and Y2.
The poverty threshold income level equals the
a. average income of the bottom one-tenth of all income recipients. b. cost of an economical and nutritional food plan for a family multiplied by six. c. cost of an economical and nutritional food plan for a family multiplied by three. d. average income of a family headed by a worker who has been unemployed for six months or more.