Refer to the given data. We can conclude that:
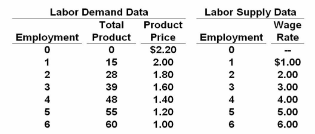
Use the resource demand data shown on the left and the resource supply data on the right in answering the following question:
A. both the product and resource markets are imperfectly competitive.
B. the resource market is imperfectly competitive, but the product market is purely
competitive.
C. both the resource and product markets are purely competitive.
D. the resource market is purely competitive, but the product market is imperfectly
competitive.
A. both the product and resource markets are imperfectly competitive.
You might also like to view...
Inclusive property rights provide an investor:
a. more options and greater incentives to avoid inefficient choices. b. an insight to future earnings and revenue generation. c. a definite return on the investment. d. cost effective techniques of production leading to economies of scale.
Which of the following would not be counted in the U.S. balance of payments' current account?
a. Helen, an American oil engineer, is a paid adviser to Mexico. b. Exxon owns oil fields in Mexico. c. France purchases a new jet fighter aircraft from the Boeing Company in Seattle. d. Martha receives a $50 dividend check on stock she owns in a business in Mexico. e. A wealthy Italian purchases numerous antiques in the United States for his Roman villa.
Which of the following statements is true concerning comparative advantage?
A. Rich nations typically have a comparative advantage in the production of all goods. B. Poor nations typically have a comparative advantage in the production of all goods. C. Poor nations typically have a comparative advantage in high-tech but not agricultural goods. D. Poor nations typically have a comparative advantage in agricultural but not high-tech goods.
Financial intermediaries are:
A. government officials who bring together buyers and sellers in a market. B. those who negotiate terms of settlement between borrower and lender when one is in default. C. institutions that channel funds from people who have them to people who want them. D. those who negotiate terms of settlement between buyer and seller when one is in default.