A 5.0-g particle moving 60 m/s collides with a 2.0-g particle initially at rest. After the collision each of the particles has a velocity that is directed 30° from the original direction of motion of the 5.0-g particle. What is the speed of the 2.0-g particle after the collision?
A. 72 m/s
B. 87 m/s
C. 79 m/s
D. 94 m/s
E. 67 m/s
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
A 4.0-kg mass has a velocity of 4.0 m/s, east when it explodes into two 2.0-kg masses. After the explosion one of the masses has a velocity of 3.0 m/s at an angle of 60° north of east. What is the magnitude of the velocity of the other mass after the explosion?
a. 7.9 m/s b. 8.9 m/s c. 7.0 m/s d. 6.1 m/s e. 6.7 m/s
A gold brick measuring 0.25 ft by 0.33 ft by 1 ft is submerged in water. The weight density of gold is 1,200 pounds per cubic foot and the weight density of water is 62.4 pounds per cubic foot. (a) What is the weight of the gold brick? (b) What is the buoyant force on the gold brick? (c) What is the net force on the gold brick?
In the inner solar system, the largest surface features (such as volcanoes or valleys) are found on the largest planets
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
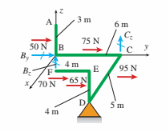
Each y-direction force on frame ABCDEF below acts at the center of the bar segment to which it is applied. Support B is restrained against translation in the y and z directions only, and support C is restrained in the z direc- tion only. Support D is a pin support. Equilibrium of the frame requires that reaction force Cz is (in newtons):
(A) 80.8 N
(B) 67.7 N
(C) 14.8 N
(D) 92.2 N