Price discrimination refers to:
A. selling a given product for different prices at two different points in time.
B. any price above that which is equal to a minimum average total cost.
C. the selling of a given product at different prices to different customers that do not reflect
cost differences.
D. the difference between the prices a purely competitive seller and a purely monopolistic
seller would charge.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Assume a market is producing efficiently. Which type of government intervention in this market might create a deadweight loss?
i. a price ceiling ii. a price floor iii. a price support A) i only B) i and ii C) iii only D) ii and iii E) i, ii, and iii
The linear regression equation, Y = a + bX, was estimated. The following computer printout was obtained: 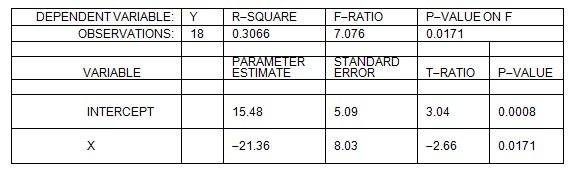 Given the above information, which of the following statements is correct at the 1% level of significance?
Given the above information, which of the following statements is correct at the 1% level of significance?
A. â is statistically significant, but b? is not. B. b? is statistically significant, but a? is not. C. Neither â nor b? is statistically significant. D. Both â and b? are statistically significant.
Contractionary monetary policy tends to:
A. reduce the interest rate, increase capital inflows, and lower the value of the dollar. B. raise the interest rate, reduce capital inflows, and raise the value of the dollar. C. reduce the interest rate, reduce capital inflows, and lower the value of the dollar. D. raise the interest rate, raise capital inflows, and raise the value of the dollar.
President George W. Bush used part of the budget surplus inherited from the Clinton administration to:
A. fund tax cuts. B. stimulate the economy that was slowing down following the end of the high-tech investment boom. C. increase government entitlement spending. D. both fund tax cuts and stimulate the economy that was slowing down following the end of the high-tech investment boom.