If the Consumer Price Index (CPI) increases from 100 to 125 and the nominal wage increases from $125 to $300, what is the change in the real wage?
a. +$175
b. +$300
c. +$125
d. +$115
e. -$175
D
You might also like to view...
Assume that foreign capital flows from a nation increase due to political uncertainly and increased risk. If the nation has highly mobile international capital markets and a fixed exchange rate system, what happens to the real risk-free interest rate and real GDP in the context of the Three-Sector-Model? a. The real risk-free interest rate rises and real GDP falls
b. The real risk-free interest rate falls and real GDP rises. c. The real risk-free interest rate rises and real GDP remains the same. d. The real risk-free interest rate and real GDP remain the same. e. There is not enough information to determine what happens to these two macroeconomic variables.
Which of the following best completes the sentence; "Under a gold standard a central bank … "?
A. will have gold reserves depleted when exports exceed imports. B. wants to keep their gold reserves fixed. C. can have too little gold but never have too much. D. can have too much gold.
The full-employment level of real GDP is the level which can be produced with:
a. both given technology and productive resources, and cyclical unemployment equal to zero. b. both given technology and productive resources, and frictional and structural unemployment equal to zero. c. given technology and productive resources. d. frictional and structural unemployment equal to zero. e. cyclical unemployment equal to zero.
Refer to the information in Figure 16.5 below to answer the question(s) that follow.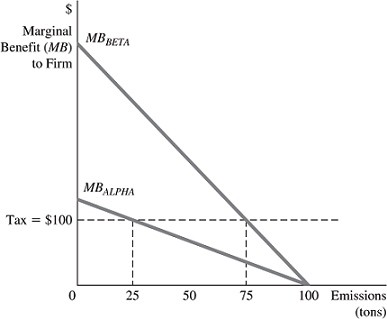 ?Figure 16.5Figure 16.5 shows the marginal benefits of emitting pollution for the only two chemical companies in an industry, Alpha Chemicals and Beta Chemicals. Before any tax on pollution emissions is imposed, each company views pollution as being free.Refer to Figure 16.5. Suppose that instead of a tax, the government uses standards to achieve the emission reductions, requiring that each company cut its original emissions in half rather than allowing each company to choose emissions based on their costs. Compared to the outcome under the tax, this common standard would
?Figure 16.5Figure 16.5 shows the marginal benefits of emitting pollution for the only two chemical companies in an industry, Alpha Chemicals and Beta Chemicals. Before any tax on pollution emissions is imposed, each company views pollution as being free.Refer to Figure 16.5. Suppose that instead of a tax, the government uses standards to achieve the emission reductions, requiring that each company cut its original emissions in half rather than allowing each company to choose emissions based on their costs. Compared to the outcome under the tax, this common standard would
result in A. Alpha gaining less than Beta loses. B. Beta gaining less than Alpha loses. C. Alpha gaining more than Beta loses. D. Beta gaining more than Alpha loses.