Cost-push inflation arises from:
A. an increase in aggregate supply.
B. a decrease in aggregate demand.
C. a decrease in aggregate supply.
D. an increase in aggregate demand.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
A scatter diagram with the price of vacations to Mexico on the vertical axis and the price of vacations to California on the horizontal axis shows a positive relationship
If the price of vacations to Mexico were placed on the horizontal axis, and the price of vacations to California on the vertical axis, the relationship would be A) negative relationship, also called a direct relationship. B) negative relationship, also called an inverse relationship. C) positive relationship, also called a direct relationship. D) positive relationship, also called an inverse relationship.
Suppose milk and cereal are compliments and the demand for milk is Qdm = 40 - 6Pm - 2Pc, where Qdm stands for millions of gallons of milk demanded, Pm stands for the price of milk and Pc stands for the price of cereal. The supply of milk is Qsm = 6Pm - 8, where Qsm stands for millions of gallons of milk supplied. The demand and supply of cereal are Qdc = 90 - 5Pc - Pm and Qsc = 5Pc - 10, respectively, where Qdc stands for millions of boxes of cereal demanded and Qsc stands for millions of boxes of cereal supplied. Which of the following gives the market-clearing curve for milk?
A. Pm = 4 - (Pc/6) B. Pm = (32/12) - (Pc/6) C. Pm = (32 - 2Pc)/12 D. Pm = (32/12) + (Pc/6)
Built-in stabilizers
A. are insufficient to prevent the business cycle, but tend to lessen fluctuations in real GDP. B. were introduced under President Nixon. C. are found primarily in discretionary fiscal policy. D. tend to lessen fluctuations in GDP through their effect on the money supply. E. were endorsed by Adam Smith.
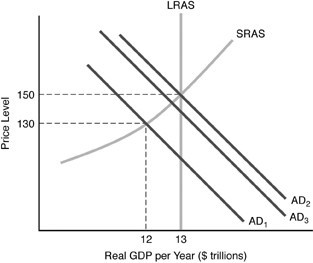 Refer to the above figure. Suppose that the economy starts at AD1. If the government reduces taxes, then the economy goes to AD2, but then falls back to AD1. This is an example of
Refer to the above figure. Suppose that the economy starts at AD1. If the government reduces taxes, then the economy goes to AD2, but then falls back to AD1. This is an example of
A. the free rider problem. B. laissez-faire. C. complete crowding-out effect. D. partial crowding-out effect.