Refer to the consumption schedule above. Disposable income equals consumption at point:
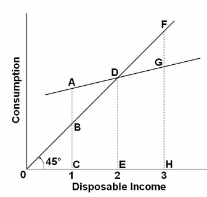
A. A
B. C
C. D
D. G
C. D
You might also like to view...
Refer to Table 4-2. The table above lists the highest prices five consumers are willing to pay for a theater ticket. If the price of one ticket is $25
A) no one will buy a ticket. B) Anya's consumer surplus is $1. C) everyone will buy a ticket. D) consumer surplus will be maximized.
Always There Wireless is wireless monopolist in a rural area. There are 200 customers, each of whom has a monthly demand curve for wireless minutes of Qd = 200 - 100P, where P is the per-minute price in dollars and Q is the number of wireless minutes. The marginal cost of providing the wireless service is $0.25 per minute. If Always There charges $0.50 per minute and the largest fixed fee that it can at that price, what is the difference in profit per customer compared to when it charges $0.25 per minute and the largest fixed fee that it can at that price?
A. Profit per customer is the same in both cases, and it is equal to zero. B. Profit per customer is the same in both cases, and it is positive. C. Profit is $3.13 per customer higher at a price of $0.50. D. Profit is $3.13 per customer higher at a price of $0.25.
Explain why the marginal propensity to save and the marginal propensity to consume sum to 1
According to classical economists,
a. full employment means zero unemployment b. as long as markets clear, no government action is needed to ensure full employment c. even if all markets clear, government action is needed to correct labor market imperfections if the economy is to reach full employment d. as long as markets clear and government provides jobs to those who need them, the economy will be at full employment e. even if markets clear, cyclical unemployment will still persist in the long run