for the case when the motor frequency is reduced to 50 Hz and the voltage sequence is reversed. Assume that the converter is a fixed v/f controller.
a. Motor current before the countercurrent braking
b. Motor current just after the voltage sequence is reversed
c. Current at the moment when the motor stops
d. Motor torque at the condition of part (c)
e. Motor current at the new steady-state point
f. Motor torque at the new steady-state point
g. Motor speed at the new steady-state point
Solution:
From Problem 10.5,
60 Hz, 4-pole, 480 V, 3-phase, Y-connected induction machine
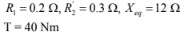
From Problem 10.5, two things have changed:
Ns = 50*60/2 = 1500 rpm
Xeq = 12*50/60 = 10 ohms
Therefore, to find the current, the slip has to be found first:
Using the small slip approximation
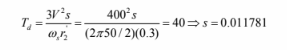
a.
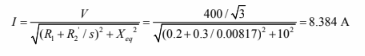
b. After the sequence is reversed, the slip is
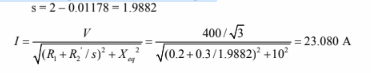
c. Current at the moment the motor stops:
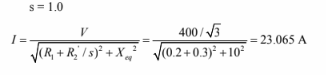
d. Motor torque in c.
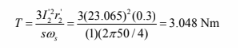
e. Motor current at the new steady state point:
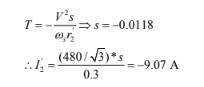
f. Motor torque at the new steady state point:
T = 40 Nm
g. Motor speed at the new steady state point:
n = 60*50/2*(1 + 0.0118) = 1517.7 rpm
You might also like to view...
What are the two advantages of draining the condensed moisture to the slinger system on the condenser?
What will be an ideal response?
When performing a battery load test, how many seconds should the load be applied?
A) 15 B) 60 C) 5 D) 10
How are quality costs used for decision-making?
What will be an ideal response?
By using the 1/4 scale, the drawing will be reduced to 1/48th of its full size.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)