Primary and secondary xylem that can no longer transport water and solutes, and can store defensive
compounds, is called
a. bark.
b. heartwood.
c. vascular cambium.
d. sapwood.
e. secondary epidermis.
B
You might also like to view...
Tetrodotoxin is a potent poison, produced by some newts, pufferfish, and blue-ringed octopus that affects sodium transport involved with the voltage gates in neurons. A friend swimming in the Caribbean is pricked by a pufferfish and gets very sick. The most likely action the poison takes is
A. Mimicking a symporter and allowing sodium to rush out and potassium to rush in. B. Mimicking an antiporter and allowing sodium to rush out. C. Blocking an antiporter so sodium cannot rush in. D. Blocking a symporter and keeping sodium from rushing in. Clarify Question · What is the key concept addressed by the question? · What type of thinking is required? Gather Content · What do you know about the effects of tetrodotoxin on ion movement in neurons? What other information is related to the question? Choose Answer · Given what you now know, what information and/or problem solving approach is most likely to produce the correct answer? Reflect on Process · Did your problem-solving process lead you to the correct answer? If not, where did the process break down or lead you astray? How can you revise your approach to produce a more desirable result?
When cells of a facultative anaerobe such as Paracoccus denitrificans are growing under anaerobic conditions and using nitrate as the terminal electron acceptor, ________ nitrate reduction is occurring.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
What is the function of the gill-like compacted hyphae on the underside of the Basidiocarp’s cap?
a. They host basidiospores. b. They allow for nitrogen fixation. c. They bear developing basidia. d. They shelter mating mycelia.
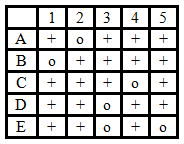
The test described here is a recombination test. Answer with TRUE or FALSE.
Shown below are the maps of a series of rII- deletion strains (1–5). The deleted region is indicated as (......) and the intact region as ______.
1 ___________(...........)_______________
2 _________________(...........)_________
3 (.....................)_____________________
4 ________________________(................)
5 _____(..........)______________________
rII- phage strains A-E have point mutations in the rII region. E.coli K(?) cells are coinfected with one phage that has a deletion and one phage that has a point mutation. The presence of wild-type progeny phage is assessed by the presence (+) or absence (o) of plaques.