A moment before, you were enveloped in a bright plasma. You could not see very far as free electrons zipped around your head, scattering photons. But now, the universe has suddenly become transparent and you can see clearly
There seem to be no planets or stars, only a gas filled with mostly neutral hydrogen atoms. Where are you?
A) You are in the universe about 5 minutes after the Big Bang just as the nucleosynthesis era is ending.
B) You are in intergalactic space within a rich cluster of galaxies.
C) You are in the universe when it was about 500 million years old, just before galaxies began to form.
D) You are in the universe about 380,000 year after the Big Bang during the formation of the cosmic background radiation.
E) You are in a closed universe just as it begins to re-collapse.
D
You might also like to view...
Saturated steam at 137 kPa condenses on the outside of a 2.6-m-length of copper tubing heating 5 kg/hr of water flowing in the tube. The water temperatures, measured at 10 equally spaced stations along the tube length are

Calculate (a) average overall heat transfer coefficient Uo based on the outside tube area;
(b) average water-side heat transfer coefficient hw (assume steamside coefficient at
hs = 11,000 W/(m2 K)), (c) local overall coefficient Ux based on the outside tube area for
each of the 10 sections between temperature stations, and (d) local waterside coefficients
hwx for each of the 10 sections. Plot all items vs. tube length. Tube dimensions: ID = 2 cm,
OD = 2.5 c. Temperature station 1 is at tube entrance and station 11 is at tube exit.
GIVEN
? Saturated steam condensing on copper tubing with water flowing within
? Steam pressure = 1.35 atm = 136,755 N/m2
? Tube length (L) = 2.6 m
? Water flow rate mw = 5 kg/h = 0.00139 kg/s
? Water temperatures given above as a function of distance along pipe
? Tube diameters
? Di = 2 cm = 0.02 m
? Do = 2.5 cm = 0.025 m
FIND
(a) Average overall heat transfer coefficient based on the outside tube area (Uo)
(b) Average water-side transfer coefficient hw
(c) Local overall coefficient (Ux) for each of the 10 sections
(d) Local water-side coefficient hwx for each of the 10 sections
Plot all items vs. tube length
ASSUMPTIONS
? The steam-side heat transfer coefficient hs = 11,000 W/(m2 K)
? No scaling resistance
? Variation of the specific heat of water is negligible
SKETCH
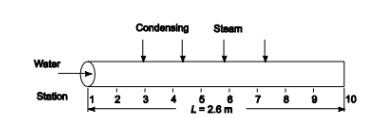
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
From Appendix 2, Table 13, for saturated steam at 136,755 N/m2: Ts = 107°C
For water at the average temperature of 55°C, the specific heat (cpw) = 4180 J/(kg K)
From Appendix 2, Table 12, the thermal conductivity of copper (k) = 392 W/(m K) at 127°C
What is the half-life of a radioactive isotope?
A) the amount of time for half of a sample of the isotope to decay into a different element or isotope B) the amount of time for half of a sample of the element to decay into nothing C) half of the total time that the isotope has been in existence D) half of the amount of that element in the universe E) half of the age of the solar system
The radius R of a nucleus of mass number A is given by R = R0 A1/3, where R0 = 1.2 × 10-15 m, calculate the density of a nucleus that has contains 57 protons and 82 neutrons. The mass of a nucleon (proton or neutron) is 1.67 × 10-27 kg
What will be an ideal response?
A beam of light in air is incident on the surface of a rectangular block of clear plastic (n = 1.40). If the speed of the beam before it enters the plastic is 3.00 × 10^8 m/s, what is its speed inside the block?
a. 2.14 × 10^8 m/s c. 1.94 × 10^8 m/s b. 2.01 × 10^8 m/s d. 3.00 × 10^8 m/s