Contractionary monetary policy:
a) shifts the aggregate demand curve to the left.
b) shifts the aggregate demand curve to the right.
c) does not shift the aggregate demand curve.
d) shifts the aggregate demand curve to the left and then back to the right.
Ans: a) shifts the aggregate demand curve to the left.
You might also like to view...
The figure above shows the market for steel, the production of which creates pollution
a. What point represents the equilibrium price and what point represents the equilibrium quantity in an unregulated, competitive market? b. What area represents the deadweight loss of the unregulated, competitive market outcome? c. What point represents the efficient quantity? d. If the output level in part (c) was achieved through the use of a government imposed tax, what price would consumers pay? What price would the producers receive? What distance represents the amount of the tax? e. If government successfully uses marketable permits to eliminate the external cost, what point represents how much output would be produced?
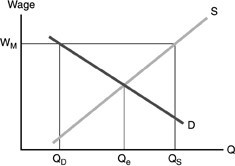 Refer to the above figure. A minimum wage has been set at WM. The amount of unemployment is
Refer to the above figure. A minimum wage has been set at WM. The amount of unemployment is
A. zero. B. at Qe. C. QS minus QD. D. not computable from the information given.
If real disposable income increases, the average propensity to consume will
A. increase. B. initially increase, and then decrease. C. decrease. D. remain constant.
An argument has been made that the shrinking deficits of the 1990s were attributable to the
A. bailout of the savings and loans. B. Gulf War. C. peace dividend that resulted from the end of the Cold War. D. Cold War.