Calculate the rate of heat loss per foot and the thermal resistance for a 15 cm schedule 40 steel pipe covered with a 7.5 cm thick layer of 85% magnesia. Superheated steam at 150°C flows inside the pipe [ ch = 170 W/(m2 K)] and still air at 16°C is on the outside [ ch = 30 W/(m2 K)].
GIVEN
A 6 in. standard steel pipe covered with 85% magnesia Magnesia thickness = 15 cm=0.15 m Superheated steam at Ts= 150°C flows inside the pipe Surrounding air temperature (T?) = 17°C Heat transfer coefficients
? Inside ( ci h ) = 170 W/(m2 K)
? Outside ( co h ) = 30 W/(m2 K)
FIND
(a) The thermal resistance (R) (b) The rate of heat loss per foot (q/L)
ASSUMPTIONS
Constant thermal conductivity The pipe is made of 1% carbon steel
SKETCH
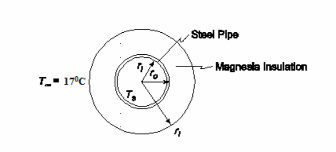
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
? Inside diameter (Di) = 6.065 in.=0.154 m
? Outside diameter (Do) = 6.625 in.=0.1683 m Thermal Conductivities
? 85% Magnesia (kI) = 0.059 W/(m K) at 20°C
? 1% Carbon steel (ks) = 43 W/(m K) at 20°C
The thermal circuit for the insulated pipe is shown below
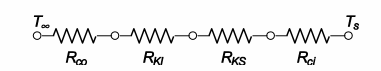
(a) The values of the individual resistances can be calculated
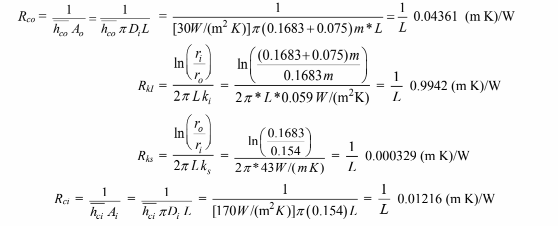
The total resistance is
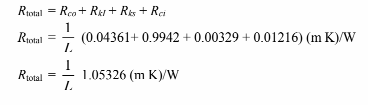
(b) The rate of heat transfer is given by
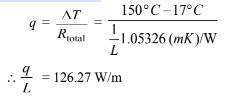
You might also like to view...
A machine that promises more energy output than input is
A) a fantasy. B) commonplace in today's technology. C) a long-shot worth investing in.
A(n) ______________ transfers heat from a low-temperature reservoir to a high-temperature reservoir
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Longitudinal seismic body waves are known by the letter ______________
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Briefly discuss the Hubble constant
What will be an ideal response?