Describe intellectual property rights. What agreements have been reached regarding their protection? What are the benefits and the costs of protecting intellectual property rights?
What will be an ideal response?
Intellectual property rights included copyright and related rights for literary and artistic work as well as industrial property rights such as trademarks and patents. TRIPS is an international agreement specifying the rules for respecting intellectual property rights as they relate to trade and was reached as part of the Uruguay Round. If intellectual property rights are not protected, it restricts trade flows. Exporters are reluctant to sell into a market if they know their ideas or brand will be stolen or copied by local firms. Research and innovation are more likely because protecting intellectual property gives financial incentives to firms and individuals to do research and continue to innovate. But protecting intellectual property rights means that high costs for enforcement are imposed on developing countries; it is not well established empirically that the benefits of innovation outweigh the costs of access, especially for developing countries that find access to new technology curtailed by having to pay royalties and fees.
You might also like to view...
When calculating the price elasticity of demand, which of the following conditions must be satisfied?
A) All other factors that influence demand must be held constant. B) Prices of related goods must be held constant but all other factors must be allowed to vary. C) Prices of related goods must be allowed to vary but all other factors must be held constant. D) All other factors than influence demand must be allowed to vary.
Using Figure 1 above, if the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD3 to AD2 the result in the short run would be: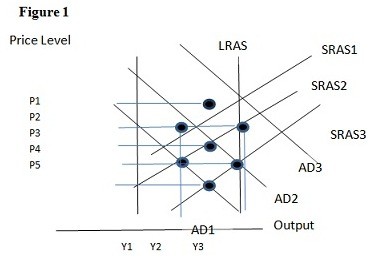
A. P3 and Y1. B. P2 and Y1. C. P2 and Y3. D. P1 and Y2.
The Gini coefficient measures:
A. income inequality. B. poverty prevalence. C. average income per person. D. change in average income per person over time.
The rational expectations hypothesis suggests that
A) people are creatures of habit and tend not to change their economic behavior in the short run. B) people are rational if they make forecasts about economic activity. C) people use all available information to make forecasts about future economic activity and adjust their behavior to these forecasts. D) people use all available information to make forecasts about future economic activity but often fail to adjust their behavior to these forecasts.