An aniline-alcohol solution is flowing at a velocity of 3 m/s through a long, 2.5 cm-ID thin-wall tube. Steam is condensing at atmospheric pressure, on the outer surface of the tube, and the tube-wall temperature is 100°C. The tube is clean, and there is no thermal resistance due to a scale deposit on the inner surface. Using the physical properties tabulated below, estimate the heat transfer coefficient between the fluid and the pipe using and compare the results. Assume that the bulk temperature of the aniline solution is 20°C and neglect entrance effects.
GIVEN
• An aniline-alcohol solution flowing through a thin-walled tube
• Tube is clean with no scaling on inner surface
• Velocity (V) =3 m/s
• Inside diameter of tube (D) = 2.5 cm = 0.025 m
• Tube wall surface temperature (Ts) = 100°C
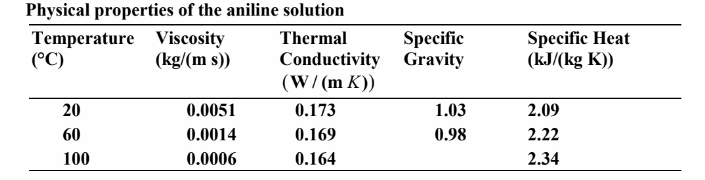
• Solution has the properties listed above
• Solution bulk temperature (Tb)= 20°C FIND
• The heat transfer coefficient ( ch ) using: (a) Equation (7.61) (b) Equation (7.66)
ASSUMPTIONS
• Steady state
• Entrance effects are negligible
• Thermal resistance of the tube is negligible
• Tube wall temperature is constant and uniform
• Fully developed flow
SKETCH

PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
The density of water ? 1000 kg/m3
The kinematic viscosity (?) of the solution at the bulk temperature is

The Prandtl number is
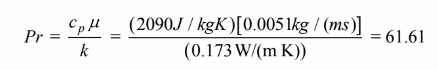
The Reynolds number is
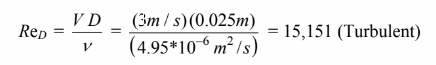
(a) Applying the Dittus-Boelter correlation
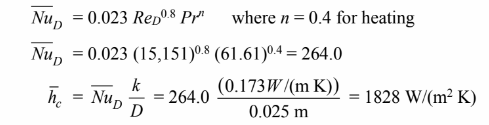
(b) Using the Sieder-Tate correlation

COMMENTS
These estimates vary by about 3% around an average value of 1828 W/(m2 K). But the Sieder-Tate
correlation is more applicable in this case because it takes the large variation of the viscosity with
temperature into account.
Note that the above correlations require that all properties (except ?s) be evaluated at the bulk
temperature.
You might also like to view...
Two piano strings are simultaneously played – their mass and length are identical, but the tensions differ. If the first string resonates with a fundamental frequency of 330 Hz, and its tension is 1.2% greater than that of the second string, what is the fundamental frequency of the second string?
A. 328 Hz B. 326 Hz C. 336 Hz D. 334 Hz
Toward which point of the compass does Toledo move as a result of the Earth's rotation?
What will be an ideal response?
How do observations of galaxies at different distances help us learn about galaxy evolution?
A) Observations of different distances show galaxies of different ages and therefore different stages of evolution. B) Observations of the most distant galaxies will allow us to observe the birth of galaxies. C) We can observe galaxies at different distances merge, helping us learn how mergers affect evolution. D) We can observe the evolution of a single galaxy over time. E) We can see what our galaxy used to look like over time, helping us theorize about the physical processes that led to its current appearance.
Sodium hydroxide, NaOH, is a strong base, which means that it readily accepts hydrogen ions. What products are formed when sodium hydroxide accepts a hydrogen ion from a water molecule?
A) water and sodium hydroxide B) sodium hydroxide and hydronium ions C) sodium ions and hydronium ions D) sodium ions and water