The supply curve for a perfectly competitive market:
A. is the summation of all the average cost curves of each firm in a market.
B. is the summation of all the marginal cost curves, above the minimum of the average variable cost curve, from all the individual firms in the market.
C. is not related to the supply curves of individual firms.
D. is independent of price.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
The prediction that workers get additional training only when the rewards from the training are expected to exceed the costs of the training (including the opportunity costs) is based on the:
A. cost-benefit principle. B. principle of comparative advantage. C. principle of diminishing returns to capital. D. scarcity principle.
What is the most important factor that explains differences in living standards across countries?
a. the quantity of money b. the level of unemployment c. productivity d. equality
Figure 7-17
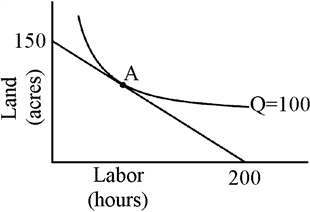
Which of the following statements must be true when a firm makes choices that put it at point A in Figure 7-17?
a.
The firm is minimizing its cost of producing 100 units of output.
b.
The ratio of the marginal physical products of labor and of land equals the ratio of the prices of labor and of land.
c.
The firm first decided how much output to produce and then decided how to produce it.
d.
All of the above are true.
The international adjustments, which will help the U.S. economy out of a structural stagnation, include:
A. running expansionary policies to shift the aggregate demand curve to the right. B. hiring workers in the government sector to boost employment. C. depreciating the value of the dollar. D. extending unemployment compensation to replace income for unemployed workers.