Dephosphorylation of the adenosine triphosphate molecule (shown in this diagram) generally results in only the removal of the Gamma phosphate and Beta phosphate groups, leaving the Alpha phosphate group bonded to the adenosine molecule. How can you explain this behavior?
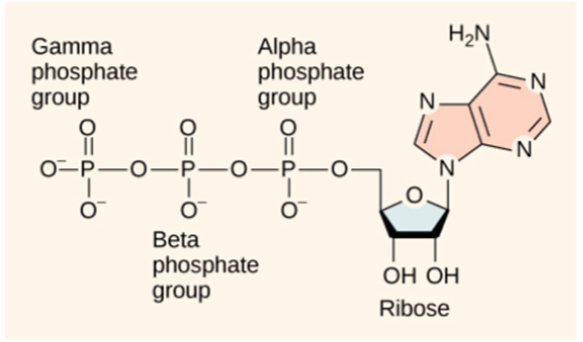
a. The enzymes that catalyze dephosphorylation reactions become saturated after bonding with two phosphate groups and cannot bond to a third.
b. After two phosphate groups are removed from ATP, the resulting solution is too acidic to sustain additional dephosphorylation reactions.
c. Without the repulsive forces generated between phosphate groups, the adenosine monophosphate molecule is much more stable.
d. Dephosphorylation can proceed with the Alpha phosphate group, but cells only require the energy released from Gamma and Beta phosphate groups.
c. Without the repulsive forces generated between phosphate groups, the adenosine monophosphate molecule is much more stable.
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is TRUE of fate mapping?
A. It determines the ultimate structure/function of a particular cell type during embryonic development. B. It maps the genes of an embryo. C. It assesses the quality of a developing embryo. D. It maps the proteins within a morphogenic field. E. It determines hereditable disorders in the embryo.
Which of the following is true about binary fission?
a. It is thought to have evolved from mitosis. b. It is used in gamete formation. c. It results in the production of two identical daughter cells. d. It requires spindle formation. e. It is used during eukaryotic cell growth.
All members of a cohort are the same _____
a. sex c. age b. size d. weight
The genes for zeste eyes and forked bristles are located on the X chromosome in Drosophila melanogaster. Both genes are recessive. A cross is made between a zeste-eyed female and a forked-bristled male
(a) If 200 offspring from this cross were obtained, present the expected number, sex, genotype, and phenotype in each class of the F1. (b) If the F1 offspring were crossed to produce 800 flies of an F2 generation, present the expected number, sex, and phenotype in each class. Assume no crossing over.