Suppose you look at a detailed spectrum of visible light from some object. How can you decide whether it is an emission line spectrum or an absorption line spectrum?
A) An emission line spectrum consists of bright lines on a dark background, whereas an absorption line spectrum consists of dark lines on a rainbow background.
B) An emission line spectrum consists of a long bright line, whereas an absorption line spectrum consists of a long dark line.
C) The only way to decide is to make a graph of the intensity of the light at every wavelength, and then analyze the graph carefully.
D) The emission line spectrum is produced by electrons jumping up in energy level, whereas the absorption line spectrum is produced by electrons jumping down in energy level.
A) An emission line spectrum consists of bright lines on a dark background, whereas an absorption line spectrum consists of dark lines on a rainbow background.
You might also like to view...
Nuclear Reactions: Determine the missing product X in the following nuclear reaction: 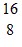 O + neutron ? X + alpha particle
O + neutron ? X + alpha particle
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
In the riddle, what is meant by light leaving its trap?
A: Light travelled much slower than the speed of light after the time of nucleosynthesis. B: Light was stuck to the matter concentrations by the force of gluons. C: Black holes prevented light from escaping in the early universe until after recombination. D: The universe was opaque until atoms formed and radiation could travel freely through space. E: The electromagnetic force held light in its place since light has an opposite charge to matter.
A weather balloon contains 12.0 m3 of hydrogen gas when the balloon is released from a location at which the temperature is 22.0°C and the pressure is 101 kPa The balloon rises to a location where the temperature is -30.0°C and the pressure is 20.0 kPa. If the balloon is free to expand so that the pressure of the gas inside is equal to the ambient pressure, what is the new volume of the balloon? Assume that in both cases the hydrogen gas is in thermal equilibrium with the outside air.
A) 14.0 m3 B) 2.38 m3 C) 49.9 m3 D) 82.6 m3 E) 4.16 m3
Suppose a ball is dropped from shoulder height, falls, makes a perfectly elastic collision with the floor, and rebounds to shoulder height. Compare the magnitudes of the impulses delivered to the ball by gravity and by the floor during this entire motion.
A. The floor delivers an upward impulse, but gravity does not deliver a total impulse B. The two impulses have the same magnitude C. The impulse delivered by the floor is half as large as the impulse delivered by gravity D. The impulse delivered by the floor is twice as large as the impulse delivered by gravity