Suppose that a new drug has been approved to treat a life-threatening disease. The demand for that drug is shown on the accompanying graph. Prior to approval of this drug, the only treatment for this condition was any one of several non-prescription, or over-the-counter, pain relievers. The demand for one brand of the several non-prescription pain relievers is also shown on the graph.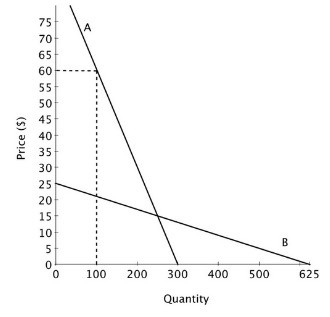 If the manufacturer of the new drug chose to increase its price from $30 to $35, consumers would buy ________ doses, and have ________ total expenditures.
If the manufacturer of the new drug chose to increase its price from $30 to $35, consumers would buy ________ doses, and have ________ total expenditures.
A. more; lower
B. fewer; higher
C. more; higher
D. fewer; lower
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Positive analysis of economic policy
A) examines the economic consequences of policies but does not address the question of whether those consequences are desirable. B) examines the economic consequences of policies and addresses the question of whether those consequences are desirable. C) generates less agreement among economists than normative analysis. D) is rare in questions of economic policy.
All of the following are ways that the government can correct for positive externalities EXCEPT
A) by subsidizing the consumption of the good. B) producing the good itself. C) by regulation. D) by assessing an effluent fee.
If a dollar invested in the United States yields the same return as a dollar's worth of yen invested in Japan, then it implies that:
a. purchasing power parity exists. b. the foreign exchange market is in equilibrium. c. the dollar/yen exchange rate is fixed. d. interest rate parity exists. e. both the currencies are pegged to a fixed amount of gold.
Suppose the exchange rate is initially set at 100 yen per dollar and increases to 125 yen per dollar. This would be expected to cause the price of U.S. goods in the Japanese economy to
A. increase. B. change in a manner that cannot be determined without additional information. C. remain the same since domestic demand remains the same. D. decrease.