A cost that is unavoidable regardless of the actions of a decision maker is called
A. a sunk cost.
B. a marginal cost.
C. an opportunity cost.
D. an incremental cost.
A. a sunk cost.
You might also like to view...
Which of the following increases the supply of a good and shifts its supply curve rightward?
A) a smaller number of producers B) an increase in the price of the good C) a higher wage paid to workers in the industry D) a technological advance in how the good is produced E) an increase in the cost of the resources used to produce the good
Figure 15-3
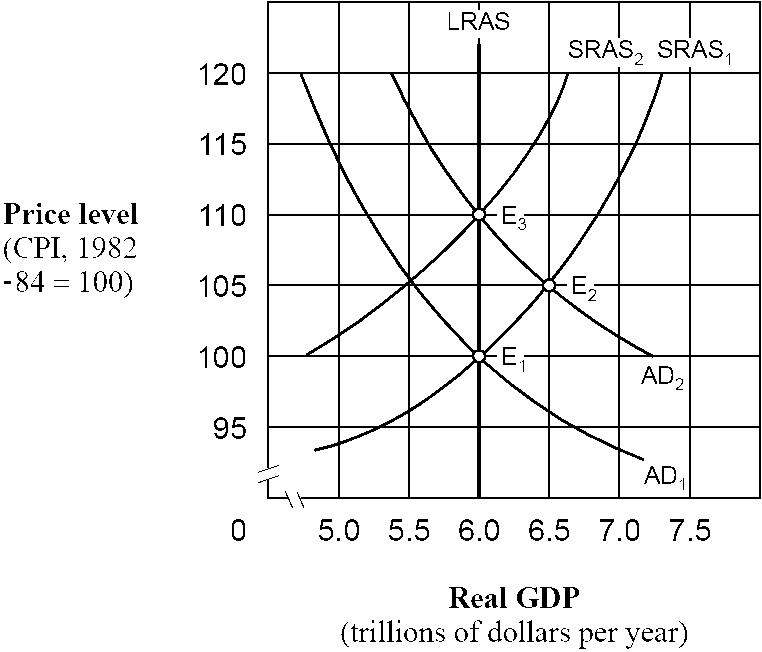
As shown in , if people behave according to rational expectations theory, an increase in the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD2 will cause the price level to move
a.
directly from 100 to 105 and then remain at 105.
b.
directly from 100 to 110 and then remain at 110.
c.
from 100 to 105 initially and then eventually move back to 100.
d.
from 100 to 105 initially and then eventually move to 110.
Beyond the provision of public goods, government exists to address:
A. national defense. B. limiting personal freedom. C. the problem of declining moral values. D. externalities and property rights.
The consumption function assumes that
What will be an ideal response?