You are working in a Drosophila lab, and find a larva with two anterior ends. Both a normal larva and the mutant larva are shown below. What is the most likely explanation for the mutant larva phenotype?
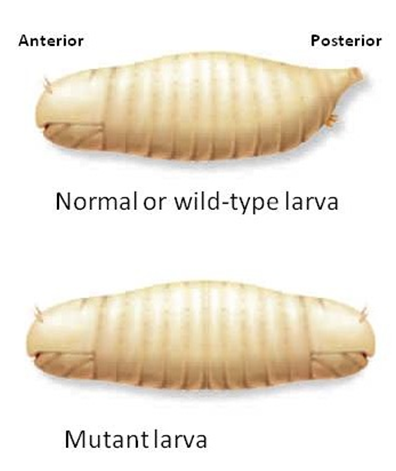
A. There is a mutation in the bicoid gene causing no functional Bicoid protein to be made.
B. The nurse cells that produce the Bicoid protein are defective, so there is no protein at either end of the embryo.
C. There is a mutation in a homeotic gene.
D. There is a high concentration of the Bicoid protein at both ends of the mutant embryo.
E. A protein encoded by a segment polarity gene is not degraded correctly and accumulates in both ends of the embryo.
D. There is a high concentration of the Bicoid protein at both ends of the mutant embryo.
You might also like to view...
The activity of some transcription factors can be regulated by covalent modifications
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
How do researchers in the metagenomics sector operate?
A) They study Mendelian traits in children. B) They link diseases by shared gene expression. C) They detect mutations in the protein encoding part of an individual's genome by using powerful algorithms. D) They collect and sequence DNA, then consult databases of known genomes to imagine what the organisms to which the DNA belongs might be like.
The plasma membrane is composed mostly of ____
a. phospholipids b. cholesterol c. triglycerides d. steroids e. sphingolipids
All of the following pertain to fluoroquinolones, except
A. they are broad spectrum. B. they are used to treat respiratory, urinary, and sexually transmitted infections. C. they are nephrotoxic. D. they are readily absorbed from intestines. E. they include ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin.