As price decreases and we move down further along a linear demand curve, the price elasticity of demand will:
a. decrease.
b. increase.
c. stay the same.
d. approach infinity.
e. increase or decrease.
a
You might also like to view...
In the above figure, when the economy is in a long-run equilibrium, real GDP will be
A) $15.5 trillion. B) $16.0 trillion. C) $17.5 trillion. D) $17.0 trillion.
Using Figure 1 above, if the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD1 to AD2 the result in the long run would be: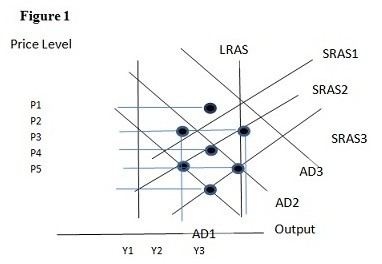
A. P1 and Y2. B. P2 and Y2. C. P3 and Y1. D. P2 and Y3.
The unemployment rate is the number of unemployed people:
A. divided by the number of people who are working. B. divided by the total working-age population. C. divided by the sum of the number of people who are working and the number of people who are looking for work. D. and the number of people working fewer than their desired number of hours, divided by the number of people who are working or looking for work.
The monopolist's marginal revenue is less than price since
A) additional units can only be sold if the price is lowered on all units sold. B) the demand function is horizontal. C) average revenue is also less than price. D) average total cost is declining.