A 15 cm black disk is placed halfway between two black 3-m-diameter disks that are 7 m apart with all disk surfaces parallel to each other. If the surroundings are 0 K, determine the temperature of the two larger disks required to maintain the smaller disk at 540°C.
GIVEN
GIVEN
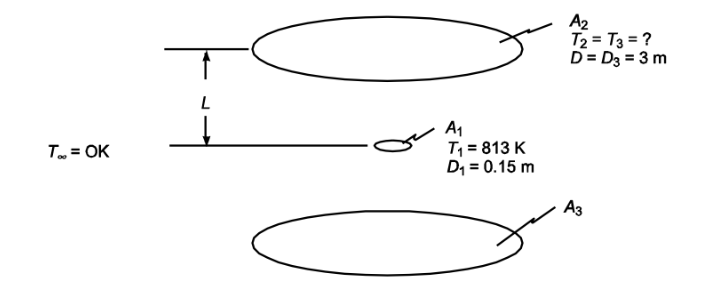
• A black disk (A1) halfway between two other black disks (A2 & A3)
• Diameter of A1 (D1) = 15 cm = 0.15 m
• Diameter of A2 and A3: (D2 = D3) = 3 m
• Distance between A2 and A3 (2L) = 7 m
• Surrounding temperature (T?) = 0 K
• Temperature of A1 (T1) = 540°C = 813 K
FIND
• The temperature A2 and A3 required ASSUMPTIONS
• A2 and A3 are at the same temperature (T2 = T3)
• Steady state conditions
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
the Stephan-Boltzmann constant (?) = 5.67 × 10–8 W/(m2 K4)
The shape factor for the geometry is
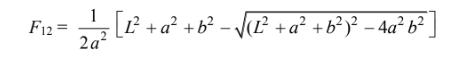
where a = D1/2 and 0.075 m b = D2/2 = 1.5 m L = 3.5 m
By symmetry F13 = F12 = 0.155.
The sum of the shape factors, including the shape factor with the surroundings must be unity
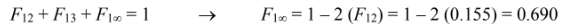
The net rate of heat transfer from A1 to A2 is
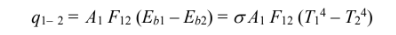
Similarly
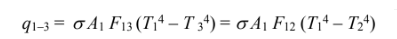

For steady state, these rates of heat transfer must sum to zero
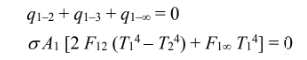
Solving for T2
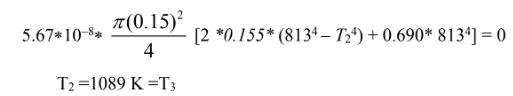
The net rate of heat transfer from A1 to A2 is
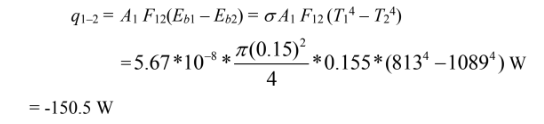
You might also like to view...
A disk is suspended by a nail such that it pivots in a vertical plane about a point on the edge of the disk. If the disk's radius is 25 cm, what is the period of oscillation?
A. 0.71 s B. Need the mass of the disk to calculate the period. C. 1.2 s D. 1.51 s
When you sit by a campfire, by what method of heat transfer are you primarily being warmed?
What will be an ideal response?
Discrete radii and energy states of atoms were first explained by electrons circling the atom in an integral number of
A) wave frequencies. B) de Broglie wavelengths. C) diffraction patterns. D) high-speed particles. E) none of the above
Three identical resistors are connected in series to a 12-V battery. What is the voltage across any one of the resistors?
A) 36 V B) 24 V C) 12 V D) 4 V E) zero