The arrow in the photo on the left points to the location of the star that has exploded as a supernova in the photo on the right. From this photo pair alone, what can we conclude about the star that exploded? (Assume that we know the star was not a member of a binary system.)
A) It was a high-mass star with at least 8 times the mass of the Sun.
B) It is now a black hole.
C) It was a red giant star.
D) Before the supernova, the star lived for at least a billion years.
A) It was a high-mass star with at least 8 times the mass of the Sun.
You might also like to view...
The electric field magnitude 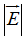 inside the wire
inside the wire
A. A B.B C.C
A rock is projected from the edge of the top of a building with an initial velocity of 12.2 m/s at an angle of 53° above the horizontal. The rock strikes the ground a horizontal distance of 25 m from the base of the building. Assume that the ground is level and that the side of the building is vertical. How tall is the building?
a. 25.3 m b. 29.6 m c. 27.4 m d. 23.6 m e. 18.9 m
Induction: A plastic rod is charged up by rubbing a wool cloth, and brought to an initially neutral metallic sphere that is insulated from ground. It is allowed to touch the sphere for a few seconds, and then is separated from the sphere by a small distance. After the rod is separated, the rod
A. is repelled by the sphere. B. is attracted to the sphere. C. feels no force due to the sphere.
In comparing our own solar system with others found to date, we find:
A) most orbits are less circular than the orbits of planets around our Sun. B) jovians often lie much closer to their suns than ours do. C) multiple planets are found in some systems. D) hot Jupiters, even closer to their stars than Mercury is to our Sun. E) All of the above