The Doppler shift is the same if the emitting object is moving toward you at some speed, or you (the observer) are moving toward it at that speed and it is still.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
True
You might also like to view...
Chondritic meteorites provide important clues because they are believed to
A. contain grains from the first material that condensed out of the Solar nebula. B. be the only source of the necessary amino acids required for life. C. be the source of all coal found on Earth. D. contain many rare metals.
Why can't Venus's atmosphere break up into small cyclonic storms, like Earth? a. Venus rotates too slowly
b. Venus rotates backwards. c. Venus has a long orbital period. d. Venus has too much CO2 in its atmosphere. e. Venus has no ozone layer to support cyclonic storms.
A solid insulating sphere of radius 5 cm carries electric charge uniformly distributed throughout its volume. Concentric with the sphere is a conducting spherical shell with no net charge as shown in Figure OQ24.9. The inner radius of the shell is 10 cm, and the outer radius is 15 cm. No other charges are nearby. Rank the magnitude of the electric field at points A (at radius 4 cm), B (radius 8
cm), C (radius 12 cm), and D (radius 16 cm) from largest to smallest. Display any cases of equality in your ranking.
A composite refrigerator wall is composed of 5 cm of corkboard sandwiched between a 1.2 cm thick layer of oak and a 0.8 mm thick layer of aluminum lining on the inner surface. The average convective heat transfer coefficients at the interior and exterior wall are 11 and 8 W/(m2 K), respectively. (a) Draw the thermal circuit. (b) Calculate the individual resistances of the components of this composite wall and the resistances at the surfaces. (c) Calculate the overall heat transfer coefficient through the wall. (d) For an air temperature of -1 0C inside the refrigerator and 32°C outside, calculate the rate of heat transfer per unit area through the wall.
GIVEN
• Refrigerator wall: oak, corkboard, and aluminum
• Thicknesses
? Oak (Lo) = 1.2 cm= 1.2*10-2 m
? Corkboard (Lc) = 5 cm= 5*10-2 m
? Aluminum (La) = 0.8 mm = 8*10-4 m
• Convective heat transfer coefficients
? Interior ( ci h ) = 12 W/(m2 K)
? Exterior ( co h ) = 8 W/(m2 K)
• Air temperature
? Inside (Ti) = -1°C
? Outside (To) = 32°C
FIND
(a) Draw the thermal circuit (b) The individual resistances (c) Overall heat transfer coefficient (U) (d) Rate of heat transfer per unit area (q/A)
ASSUMPTIONS
• One dimensional, steady state heat transfer
• Constant thermal conductivities
• Contact resistance between the different materials is negligible
SKETCH
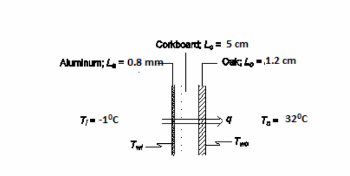
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
Oak (ko)= 0.19 W/(m K) at 20°C
Corkboard (kc) = 0.0415 W/(m K) at 20°C
Aluminum (ka) = 236 W/(m K) at 0°C