An individual plans to borrow a sum of $10,000 for one year. The nominal interest charged on the borrowed sum is 6%
a. If he takes the loan, what will be the interest amount and the total amount that he would have to pay at the end of the year?
b. If the rate of inflation in the economy is 10%, then is it a good idea for him to take the loan? Why or why not?
a. If the individual takes the loan, he will have to pay a rate of interest of 6% for the year.
Hence, interest amount = .06 × 10,000 = $600.
Total amount that he would have to pay back = $10,000 + $600 = $10,600.
b. A rational individual should make his borrowing decisions on the basis of the real interest rate and not the nominal interest rate.
Annual real interest rate in this case = 6% - 10% = -4%.
Hence, for every $100 that he borrows, after adjusting for inflation, he is actually paying back $96 after the end of the year. Hence, borrowing at an annual nominal interest rate of 6% when the annual rate of inflation is 10% is a good idea, and he should take the loan.
You might also like to view...
A major disadvantage of a proprietorship is that the ________
A) owner's entire wealth is at risk B) profits are taxed twice C) firm has perpetual life D) owner has limited liability
The size of the spread that a dealer will quote for a foreign exchange transaction will vary depending on
A) the degree of market volatility at the time. B) the degree of risk associated with a particular currency. C) the size of the market for the currency being traded. D) All of above.
When a government subsidy is granted to the sellers of a product, buyers can end up capturing some of the benefit because
a. the market price of the product will fall in response to the subsidy. b. the market price of the product will rise in response to the subsidy. c. the market price of the product will not change in response to the subsidy. d. producers will reduce the supply of the product.
Refer to the accompanying figure. In this market, equilibrium price is ________ and equilibrium quantity is ________.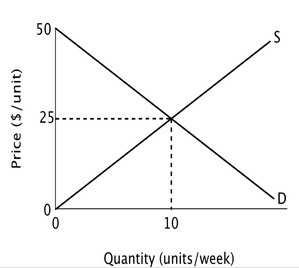
A. $50; 20 B. $25; 10 C. $20; 50 D. $10; 25