What is the opportunity cost of going from point E to point D?
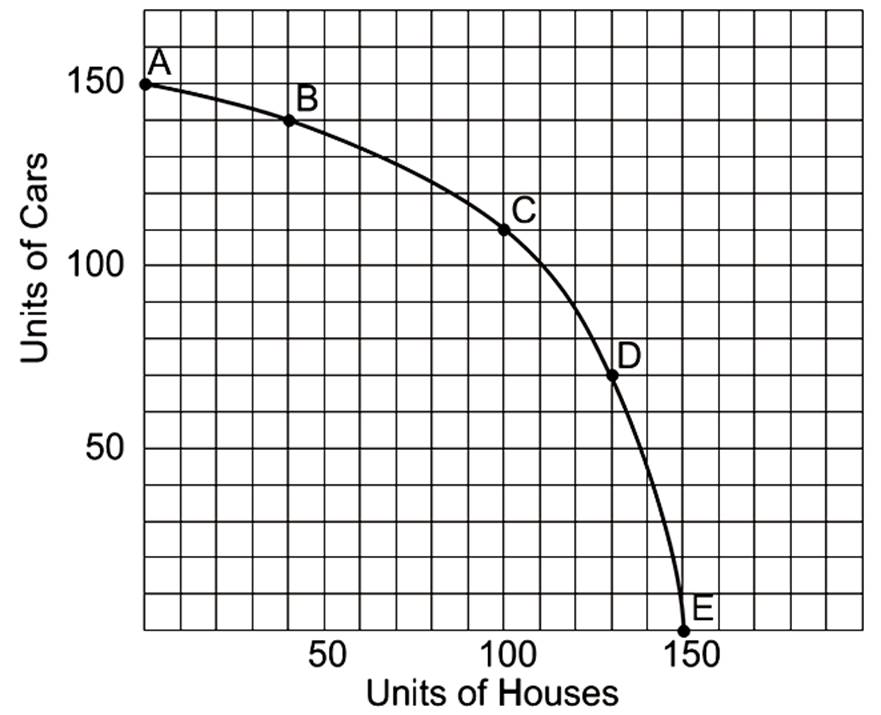
20 houses
You might also like to view...
Relative to a single price monopolist, a price discriminating monopolist generates:
A. more total surplus. B. the same amount of total surplus, but higher profits. C. less total surplus. D. the same amount of total surplus, but lower profits.
If a game has a pure strategy Nash equilibrium then
A) it might also have a mixed strategy equilibrium. B) it does not have a mixed strategy equilibrium. C) at least one player has a dominant strategy. D) no player has a dominant strategy.
The amount of money actually received in a particular period is called:
A. nominal income. B. real income. C. a cost-of-living index. D. consumer surplus.
Suppose that a new drug has been approved to treat a life-threatening disease. The demand for that drug is shown on the accompanying graph. Prior to approval of this drug, the only treatment for this condition was any one of several non-prescription, or over-the-counter, pain relievers. The demand for one brand of the several non-prescription pain relievers is also shown on the graph.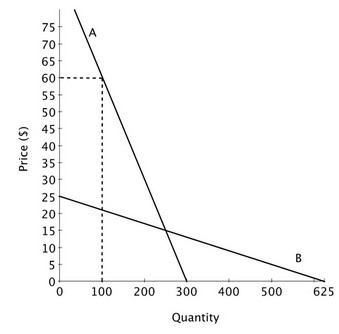 At a price of $15 (the price at which the two demand curves intersect), the price elasticity of demand for the new drug is ________ the price elasticity of demand for the over-the-counter pain reliever.
At a price of $15 (the price at which the two demand curves intersect), the price elasticity of demand for the new drug is ________ the price elasticity of demand for the over-the-counter pain reliever.
A. greater than B. the same as C. the reciprocal of D. less than