Figure 2-8
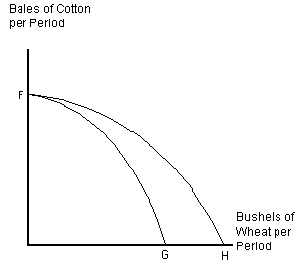
The production possibility frontier in assumes that U.S. agricultural land is used either to raise cotton for clothing or to grow wheat. This is an example of a(n)
a.
critical assumption
b.
optimizing assumption
c.
assumption of scarcity
d.
simplifying assumption
e.
realistic assumption
Assume that U.S. agricultural land is used either to raise cotton for clothing or to grow wheat. Curve FG in represents the current production possibilities frontier for cotton and wheat. What could cause the production possibilities frontier to shift from FG to FH?
a.
a change in government subsidies that favors wheat production over cotton production
b.
development of a new fertilizer that improves production of wheat, but has no impact on cotton production
c.
development of a new fertilizer that improves production of cotton, but has no impact on wheat production
d.
newly reclaimed swampland that is equally suited to growing
d
You might also like to view...
The relationship between the aggregate demand curve and the aggregate expenditures model is derived from the fact that a(n) ________.
A. decrease in the price level shifts the aggregate expenditures schedule downward and decreases equilibrium GDP B. increase in the price level shifts the aggregate expenditures schedule downward and increases equilibrium GDP C. increase in the price level shifts the aggregate expenditures schedule upward and decreases equilibrium GDP D. decrease in the price level shifts the aggregate expenditures schedule upward and increases equilibrium GDP
If the price of orchids falls, the substitution effect due to the price change will cause
A) an increase in the quantity of orchids demanded. B) an increase in the demand for roses, a substitute for orchids. C) an increase in the quantity of orchids supplied. D) an increase in the demand for orchids.
Why is there a price markup over marginal cost in monopolistic competition?
What will be an ideal response?
If the marginal cost of producing steel exceeds the marginal utility of using steel, then for economic efficiency,
a. the price of steel should fall. b. society should produce less steel. c. the price of goods made with steel should fall. d. society should direct resources toward steel production and away from the production of other goods.