Consider a firm with constant marginal cost that behaves competitively. A horizontal merger lowers the firm's marginal cost and causes the firm to behave like a monopoly. How does the merger affect producer's surplus, consumers' surplus, and social gain? Explain.
What will be an ideal response?
The merger will cause producer's surplus to rise. Prior to the merger, producer's surplus was zero. After the merger, the monopoly power allows the firm to charge a price in excess of its marginal cost, which allows the firm to earn positive producer's surplus. The monopoly power created by the merger will cause consumers' surplus to fall, unless the cost reduction is so large that the post-merger monopoly price is lower than the pre-merger competitive price. Social gain could either rise or fall as a result of the horizontal merger. For social gain to rise, the increase in producer's surplus must outweigh the loss in consumers' surplus.
You might also like to view...
A rule that a foreign company export a minimum percentage of its output is considered
a. local content requirement b. national treatment c. performance requirement d. most favored nation treatment e. none of the above
Since the 1970s, the percentage of total income earned by the poorest 20 percent of American families has fallen
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Refer to the graph shown. To maximize profit, this firm should produce: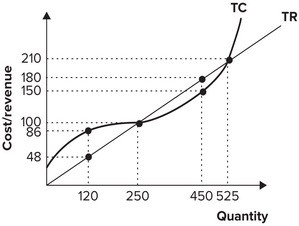
A. 250 units of output. B. 525 units of output. C. 450 units of output. D. 120 units of output.
Depreciation is
A. added to national income to get GDP. B. subtracted from national income to get GDP. C. added to GNP to get NNP. D. subtracted from GNP to get NNP.