A tax on polluting emissions will
A. provide incentives for firms to reduce the volume of polluting materials
B. raise revenue sufficient to eliminate the deficit.
C. necessarily lower the price of the products.
D. require no agency to administer the tax.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is a difference between a perfectly elastic demand curve and a perfectly inelastic demand curve?
a. A perfectly elastic demand curve is parallel to the horizontal axis, while a perfectly inelastic demand curve is parallel to the vertical axis. b. A perfectly elastic demand curve is parallel to the vertical axis, while a perfectly inelastic demand curve is parallel to the horizontal axis. c. A perfectly elastic demand curve is downward sloping, while a perfectly inelastic demand curve is upward sloping. d. A perfectly elastic demand curve is upward sloping, while a perfectly inelastic demand curve is downward sloping.
Local governments rely heavily on property taxes.
A. True B. False C. Uncertain
A temporary decrease in the price of oil would be considered a:
A. long-run supply shock. B. demand shock. C. short-run supply shock. D. The changing price of oil would not affect any of these.
Refer to the diagrams, which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing output q and the industry in which it operates. The predicted long-run adjustments in this industry might be offset by:
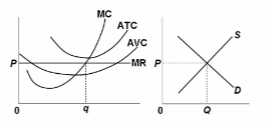
A. a decline in product demand.
B. an increase in resource prices.
C. a technological improvement in production methods.
D. entry of new firms into the industry.